Page 93 - GHES-1-2
P. 93
Global Health Econ Sustain Non-communicable diseases household survey
a p < 0.001. Figure 10 provides a clear representation of age group and rises to 1.12% in the ≥70 years of age group.
the progressive increase in the prevalence of MD with Table 11 offers insight into comorbidities among the
advancing age. It initiates at 0.39% in the 20 – 29 years of 4,244 patients with MD, revealing that 788 of them (19%)
also had other NCDs. Notably, the most prevalent NCD
comorbid with MD was HTN (7.2%).
3.6. Epilepsy
Among the 70,178 patients diagnosed with NCDs,
3,014 patients were identified as having epilepsy, resulting
in a prevalence of 0.19%. The median age for this cohort
was 24 years, with an age range from 0.3 to 100. Figure 11
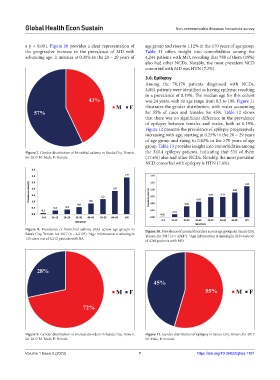
illustrates the gender distribution, with males accounting
for 55% of cases and females for 45%. Table 12 shows
that there was no significant difference in the prevalence
of epilepsy between females and males, both at 0.19%.
Figure 12 presents the prevalence of epilepsy progressively
increasing with age, starting at 0.25% in the 20 – 29 years
of age group and rising to 0.63% in the ≥70 years of age
group. Table 13 provides insight into comorbidities among
Figure 7. Gender distribution of bronchial asthma in Sana’a City, Yemen, the 3,014 epilepsy patients, indicating that 531 of them
for 2017 M: Male; F: Female. (17.6%) also had other NCDs. Notably, the most prevalent
NCD comorbid with epilepsy is HTN (7.6%).
Figure 8. Prevalence of bronchial asthma (BA) across age groups in Figure 10. Prevalence of mental disorders across age groups in Sana’a City,
Sana’a City, Yemen, for 2017 (n = 6,212*). *Age information is missing in Yemen, for 2017 (n = 4244*). *Age information is missing in 110 cases out
135 cases out of 6,212 patients with BA. of 4244 patients with MD.
Figure 9. Gender distribution of mental disorders in Sana’a City, Yemen, Figure 11. Gender distribution of epilepsy in Sana’a City, Yemen, for 2017
for 2017 M: Male; F: Female. M: Male; F: Female.
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2023) 7 https://doi.org/10.36922/ghes.1191