Page 193 - GHES-2-1
P. 193
Global Health Econ Sustain Antimicrobial resistance control model
Pre-analytical assessment Analytical assessment Post-analytical
assessment
Avoid Avoid Avoid
Incorrect analyses ordered Analytical errors Transcription errors
Incorrect test request Equipment failure Long turnaround time
Patient identification error Incorrect interpretation
Patient preparation error
Specimen mislabeling
Specimen collection error
Incorrect specimen handling
Specimen transport error
Solutions
Good microscopy
Standard phenotypic culture and
identification
Immunoassays to detect pathogen
proteins
Molecular assays to detect
pathogen nucleic acids
Sequencing for pathogen typing
Solutions Data sharing
Rejection criteria Clinical
communication
Patient’s clinical
assessment
Quality control; quality assurance; quality management system
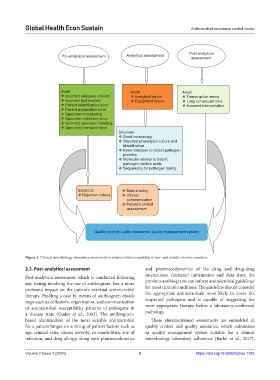
Figure 1. Clinical microbiology laboratory assessment in antimicrobial stewardship in low- and middle-income countries
2.3. Post-analytical assessment and pharmacodynamics of the drug and drug-drug
Post-analytical assessment, which is conducted following interactions. Gathered information and data from the
any testing involving the use of antibiogram, has a more previous antibiograms can inform antimicrobial guidelines
profound impact on the patient’s eventual antimicrobial for most clinical conditions. The guideline should consider
therapy. Profiling a case by means of antibiogram entails the appropriate antimicrobials most likely to cover the
steps such as collection, organization, and communication suspected pathogens and is capable of suggesting the
of antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of pathogens in most appropriate therapy before a laboratory-confirmed
a disease state (Guder et al., 2003). The antibiogram- pathology.
based identification of the most suitable antimicrobial These aforementioned assessments are embedded in
for a patient hinges on a string of patient factors such as quality control and quality assurance, which culminates
age, clinical state, illness severity, co-morbidities, site of in quality management system suitable for a clinical
infection, and drug allergy, along with pharmacokinetics microbiology laboratory adherence (Barbé et al., 2017).
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2024) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/ghes.1783