Page 196 - GHES-2-1
P. 196
Global Health Econ Sustain Antimicrobial resistance control model
Clinical microbiology
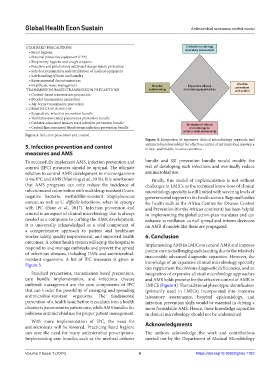
STANDARD PRECAUTIONS laboratory assessment
• Hand hygiene
• Personal protective equipment (PPE)
• Respiratory hygiene and cough etiquette
• Injection and phlebotomy safety and sharps injury prevention
• Safe decontamination and sterilization of medical equipment
• Safe handling of linen and laundry
• Environmental decontamination
• Healthcare waste management Hospital Expansive clinical Infection
prevention
TRANSMISSION-BASED TRANSMISSION PRECAUTIONS epidemiology microbiologyapproaches and control
• Contact-based transmission precaution
• Droplet transmission precaution
• Air-borne transmission precaution
COMMON CARE BUNDLES
• Surgical-site infection prevention bundle
• Ventilator-associated pneumonia prevention bundle
• Catheter-associated urinary tract infection prevention bundle Strategies of clinical
• Central-line associated bloodstream infection prevention bundle microbiology in
antimicrobial stewardship
Figure 3. Infection prevention and control.
Figure 4. Integration of expansive clinical microbiology approach and
5. Infection prevention and control antimicrobial stewardship for effective control of antimicrobial resistance
in low- and middle-income countries.
measures and AMS
To successfully implement AMS, infection prevention and bundle and SSI prevention bundle would modify the
control (IPC) measures should be optimal. The ultimate risk of developing such infections and eventually reduce
solution to control AMR development in microorganisms antimicrobial use.
is via IPC and AMS (Manning et al., 2018). It is now known Finally, this model of implementation is not without
that AMS programs can only reduce the incidence of challenges in LMICs as the technical know-how of clinical
infections and colonization with multidrug-resistant Gram- microbiology specialty is still limited with wavering levels of
negative bacteria, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus governmental support in the health sectors. Regional bodies
aureus, as well as C. difficile infections, when in synergy for health such as the Africa Centres for Disease Control
with IPC (Baur et al., 2017). Infection prevention and and Prevention (for the African continent) has been helpful
control is an aspect of clinical microbiology that is always in implementing the global action plan mandates and can
needed as a composite to curbing the AMR development. enhance surveillance, curtail spread and inform decisions
It is universally acknowledged as a vital component of on AMR if models like these are propagated.
a comprehensive approach to patient and healthcare
worker safety, quality improvement, and improved health 6. Conclusion
outcomes. A robust health system will equip the hospital to Implementing AMS in LMICs to control AMR and improve
respond to and manage outbreaks and prevent the spread patient care is challenging and daunting due to the relatively
of infectious diseases, including HAIs and antimicrobial- inaccessible advanced diagnostic capacities. However, the
resistant organisms. A list of IPC measures is given in
Figure 3. knowledge of an expansive clinical microbiology specialty
can supplement the obvious diagnostic deficiencies, and an
Standard precautions, transmission-based precautions, integration of expansive clinical microbiology approaches
care bundle implementation, and infectious disease and AMS holds promise for the effective control of AMR in
outbreak management are the core components of IPC LMICS (Figure 4). The traditional phenotypic identification
that can hinder the possibility of emerging and spreading (primarily used in LMICs) incorporated into intensive
antimicrobial-resistant organisms. The fundamental laboratory assessments, hospital epidemiology, and
prevention of a health issue before it escalates into a health infection prevention skills would be essential in driving a
disaster is paramount in patient care, while AMS handles the more formidable AMS. Hence, these knowledge capacities
judicious antimicrobial use for proper patient management. in clinical microbiology should not be undermined.
With more implementation of IPC, the need for
antimicrobials will be lowered. Practicing hand hygiene Acknowledgments
can save the need for many antimicrobial prescriptions. The authors acknowledge the work and contributions
Implementing care bundles such as the urethral catheter carried out by the Department of Medical Microbiology
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2024) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/ghes.1783