Page 194 - GHES-2-1
P. 194
Global Health Econ Sustain Antimicrobial resistance control model
A good internal and external quality assurance scheme antimicrobial treatment targeted at the most probable
should be drafted for a fully-equipped, functional clinical causative microorganism. This could be broad-spectrum
microbiology laboratory to implement a thorough AMS in antimicrobials (Vera and Luther, 2015) that drive up AMR
any institutions. External certification from registered bodies, and many other untoward consequences, such as increased
such as the International Organization for Standardization, health-care costs, adverse drug events, and sometimes
should be fostered, while the Stepwise Laboratory antibiotic-associated diarrhea. The recommendations
Improvement Process Towards Accreditation (SLIPTA) for the guideline should be based on local susceptibility
(World Health Organization Regional office for Africa, data, available scientific evidence or expert opinion when
2015) and Strengthening Laboratory Management Toward evidence is lacking.
Accreditation (SLMTA) are viable accreditation processes A drug formulary can be easily adapted from the available
readily available in LMICs that can be implemented in all antimicrobial guidelines or the nation’s existing drug
clinical microbiology laboratories to ensure quality. formulary which can reduce the use of antimicrobials not
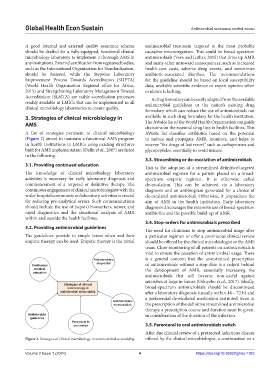
3. Strategies of clinical microbiology in available in such drug formulary for the health institution.
AMS The AWaRe list of the World Health Organization can guide
decisions on the essential drug lists in health facilities. This
A list of strategies pertinent to clinical microbiology AWaRe list classifies antibiotics based on the potential
(Figure 2) aimed to maintain a functional AMS program to induce and propagate AMR, monitors, and helps to
in health institutions in LMICs using existing structures reserve “the drugs of last resort” such as carbapenems and
built for AMS implementation (Dellit et al., 2007) are listed glycopeptides, essentially to avoid misuse.
in the following.
3.3. Streamlining or de-escalation of antimicrobials
3.1. Providing continued education
This is the adoption of a streamlined definitive/targeted
The knowledge of clinical microbiology laboratory antimicrobial regimen for a patient placed on a broad-
activities is necessary for early laboratory diagnosis and spectrum empiric regimen. It is otherwise called
commencement of a targeted or definitive therapy. The de-escalation. This can be achieved via a laboratory
continuous engagement of clinical microbiologists with the diagnosis and an antibiogram generated for a choice of
wider hospital community on laboratory activities is crucial de-escalated antimicrobial. Otherwise, it jeopardizes the
for reducing pre-analytical errors. Such communications aim of AMS in the health institution. Early laboratory
should include the use of (sepsis) biomarkers, newer, and diagnosis discourages the extensive use of broad-spectrum
rapid diagnostics and the situational analysis of AMR antibiotics and the possible build-up of AMR.
within and outside the health facilities.
3.4. Stop-orders for antimicrobials prescribed
3.2. Providing antimicrobial guidelines
The need for clinicians to stop antimicrobial usage after
The guidelines provide in simple terms when and how a particular regimen or offer a continuous clinical review
empiric therapy can be used. Empiric therapy is the initial should be offered by the clinical microbiologist or the AMS
team. Close monitoring of all patients on antimicrobials is
vital to ensure the cessation of antimicrobial usage. There
Antimicrobials is a general concern that the unrestrained prescription
stop-order of antimicrobials without a stop date is a culprit behind
Continuous
medical the development of AMR, essentially increasing the
education
antimicrobials that will become non-useful against
microbes at large in future (Oduyebo et al., 2017). Ideally,
Strategies of clinical
microbiology in broad-spectrum antimicrobials should be discontinued
antimicrobial stewardship after a laboratory diagnosis (usually within 48 – 72 h) and
a preferential de-escalated medication instituted. Even at
Antimicrobials
de-escalation the prescription of the definitive streamlined antimicrobial
therapy, a prescription course and duration must be given,
Antimicrobial in consideration of the duration of the infection.
guidelines
Parenteral to
oral switch 3.5. Parenteral to oral antimicrobials switch
After due clinical review of a protracted infectious disease
Figure 2. Strategies of clinical microbiology in antimicrobial stewardship offered by the clinical microbiologist, a continuation or a
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2024) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/ghes.1783