Page 180 - GHES-3-1
P. 180
Global Health Economics and
Sustainability
Analyzing MHTW tourism for sustainable development
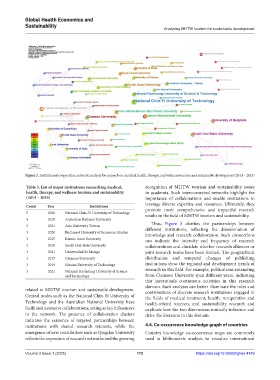
Figure 3. Institutional cooperation network analysis for research on medical, health, therapy, and wellness tourism and sustainable development (2014 – 2024)
Table 3. List of major institutions researching medical, recognition of MHTW tourism and sustainability issues
health, therapy, and wellness tourism and sustainability in academia. Such interconnected networks highlight the
(2014 – 2024) importance of collaborations and enable institutions to
leverage diverse expertise and resources. Ultimately, they
Count Year Institutions promote more comprehensive and impactful research
5 2020 National Chin-Yi University of Technology results in the field of MHTW tourism and sustainability.
4 2018 Australian National University
Thus, Figure 3 clarifies the partnerships between
3 2021 Asia University Taiwan
3 2020 Bucharest University of Economic Studies different institutions, reflecting the dissemination of
knowledge and research collaboration. Such connections
3 2015 Islamic Azad University can indicate the intensity and frequency of research
3 2018 South Ural State University collaborations and elucidate whether research alliances or
3 2021 Universidad de Malaga joint research teams have been formed. The geographical
3 2017 Clemson University distribution and temporal changes of publishing
3 2019 Silesian University of Technology institutions show the regional and development trends of
3 2021 National Kaohsiung University of Science research in this field. For example, publications emanating
and Technology from Clemson University span different years, indicating
this institution’s continuous activities in this research
domain. Such analyses can better illuminate the roles and
related to MHTW tourism and sustainable development. contributions of discrete research institutions engaged in
Central nodes such as the National Chin-Yi University of the fields of medical treatment, health, recuperative and
Technology and the Australian National University have health-related tourism, and sustainability research and
facilitated extensive collaborations, acting as key influencers explicate how the two dimensions mutually influence and
in the network. The presence of collaboration clusters drive the literature in this domain.
indicates the existence of targeted partnerships between
institutions with shared research interests, while the 4.4. Co-occurrence knowledge graph of countries
emergence of new contributors such as Qingdao University Country knowledge co-occurrence maps are commonly
reflects the expansion of research networks and the growing used in bibliometric analysis to visualize international
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2025) 172 https://doi.org/10.36922/ghes.4149