Page 109 - GPD-1-2
P. 109
Gene & Protein in Disease Exosomes connect periodontitis and systemic diseases
risk of systemic conditions, including osteoporosis [5,6] ,
kidney diseases [7,8] , Alzheimer’s disease (AD) [9,10] ,
stroke [11] , and cardiovascular diseases [12,13] . The
periodontitis insult and/or the associated pro-
inflammatory cascade could contribute to the
pathogenesis of these systemic diseases.
Chronic inflammation is driven by various mediators,
of which an important part is attributed to the interactions
within cytokine networks. Among pro-inflammatory
cytokines, interleukin (IL)-1α, IL-1β, tumor necrosis
factor alpha (TNF-α), IL-6 and IL-17 accelerate acute
and chronic inflammation, and tissue injuries; however,
other cytokines have antagonist effects which can restrain
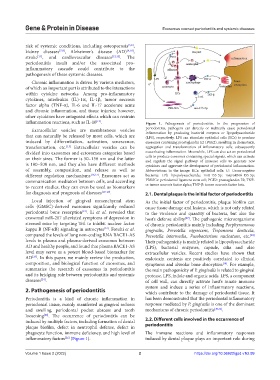
inflammation reactions, such as IL-10 . Figure 1. Pathogenesis of periodontitis. In the progression of
[14]
Extracellular vesicles are membranous vesicles periodontitis, pathogens can directly or indirectly cause periodontal
that can naturally be released by most cells, which are inflammation by producing bacterial enzymes or lipopolysaccharide
(LPS), respectively. LPS can stimulate epithelial cells (ECs) to produce
induced by differentiation, activation, senescence, exosomes containing prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), resulting in chemotaxis,
transformation, etc. [15] Extracellular vesicles can be aggregation and transformation of inflammatory cells, subsequently
divided into exosomes and ectosomes categories based exacerbating inflammation. Meanwhile, LPS can also act on periodontal
on their sizes. The former is 50–150 nm and the latter cells to produce exosomes containing special signals, which can activate
and regulate the signal pathway of immune cells to generate new
is 100–500 nm, and they also have different methods cytokines and aggravate the development of periodontal inflammation.
of assembly, composition, and release as well as Abbreviations in the image: ECs: epithelial cells; G : Gram-negative
-
different regulation mechanisms [16,17] . Exosomes act as bacteria; LPS: lipopolysaccharide; miR-155-5p: microRNA-155-5p;
communication mediators between cells, and according PDLSCs: periodontal ligament stem cell; PGE2: prostaglandin E2; TNF-
to recent studies, they can even be used as biomarkers α: tumor necrosis factor alpha; TNF-β: tumor necrosis factor beta.
for diagnosis and prognosis of diseases [18-20] . 2.1. Dental plaque is the initial factor of periodontitis
Local injection of gingival mesenchymal stem As the initial factor of periodontitis, plaque biofilm can
cells (GMSC)-derived exosomes significantly reduced cause tissue damage and lesions, which is not only related
periodontal bone resorption . Li et al. revealed that to the virulence and quantity of bacteria, but also the
[21]
exosomal miR-207 alleviated symptoms of depression in host’s defense ability . The pathogenic microorganisms
[27]
stressed mice by targeting Tril to inhibit nuclear factor of chronic periodontitis mainly including Porphyromonas
kappa B (NF-κB) signaling in astrocytes . Fotuhi et al. gingivalis, Prevotella nigrescens, Treponema denticola,
[22]
compared the levels of long non-coding RNA BACE1-AS Prevotella intermedia, Fusobacterium nucleatum, etc.
[28]
levels in plasma and plasma-derived exosomes between Their pathogenicity is mainly related to lipopolysaccharide
AD and healthy people, and found that plasma BACE1-AS (LPS), bacterial enzymes, capsule, cilia and also
level may serve as a potent blood-based biomarker for extracellular vesicles. Recent studies have shown that
AD . In this paper, we mainly review the production, endotoxin contents are positively correlated to clinical
[23]
composition, and biological function of exosomes, and symptoms and alveolar bone absorption . For example,
[29]
summarize the research of exosomes in periodontitis the main pathogenicity of P. gingivalis is related to gingival
and its bridging role between periodontitis and systemic protease, LPS, indole and organic acids. LPS, a component
diseases . of cell wall, can directly activate host’s innate immune
[24]
system and induce a series of inflammatory reactions,
2. Pathogenesis of periodontitis which contribute to the damage of periodontal tissue. It
Periodontitis is a kind of chronic inflammation in has been demonstrated that the periodontal inflammatory
periodontal tissue, mainly manifested as gingival redness response mediated by P. gingivalis is one of the dominant
and swelling, periodontal pocket abscess and tooth mechanisms of chronic periodontitis [30,31] .
[25]
loosening . The occurrence of periodontitis can be
induced by multiple factors, including formation of dental 2.2. Different cells involved in the occurrence of
plaque biofilm, defect in neutrophil defense, defect in periodontitis
phagocyte function, immune deficiency, and high level of The immune reactions and inflammatory responses
inflammatory factors (Figure 1). induced by dental plaque plays an important role during
[26]
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2022) 2 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.v1i2.99