Page 114 - GPD-1-2
P. 114
Gene & Protein in Disease Exosomes connect periodontitis and systemic diseases
exosomes and their protein contents play a significant role breach of the alveolar cortical bone, and then may result
in the pathogenesis of periodontitis. in tooth loss [100] . Obviously, osteoporosis and periodontitis
are both diseases characterized with bone resorption, and
5. Bridging role of exosomes in systemic many studies also support the hypothesis that systemic
diseases accompanied by periodontitis osteoporosis relates to local osteoporotic changes in the
[6]
Periodontal pathogenic bacteria invade periodontal tissue loss of tooth-supporting tissues, such as alveolar bone .
and cause local inflammation, and the dynamic imbalance Increasing evidence indicates that local periodontal
between pathogen and host immune response contributes inflammation can affect the bone remodeling process
to the process of periodontitis [34,97] . In the acute stage of by releasing exosomes. Zhao et al. evaluated the role of
chronic periodontitis, inflammatory periodontal tissues exosomes derived from hPDLFs in the progression of
produce many inflammatory mediators, such as IL-6, periodontitis, and the results showed that inflammatory
TNF-α, and PGE2, and release them into exosomes. hPDLFs which were pretreated with LPS can inhibit the
Subsequently, these exosomes can be transported within osteogenic activity of osteoblasts by secreting exosomes .
[96]
body fluids to various organs and tissues, thereby giving Sun et al. found that the expression of miR-214 from
rise to the corresponding response and increasing the osteoclast-derived exosomes in the serum of osteoporosis
systemic inflammatory load . A growing line of evidence patients and mice was significantly higher than that in
[98]
demonstrated that exosomes play an indispensable role in normal people and mice, the results proved that miR-214
the pathological development of various systemic diseases, could affect osteoblasts and inhibit their osteogenic activity
such as osteoporosis, kidney disease, AD, stroke, and through exosomes [101] . Proteins in exosomes may also play
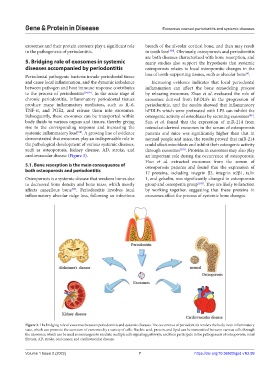
cardiovascular disease (Figure 3). an important role during the occurrence of osteoporosis.
Huo et al. extracted exosomes from the serum of
5.1. Bone resorption is the main consequence of osteoporosis patients and found that the expression of
both osteoporosis and periodontitis 17 proteins, including integrin β3, integrin α2β1, talin
Osteoporosis is a systemic disease that weakens bones due 1, and gelsolin, was significantly changed in osteoporosis
to decreased bone density and bone mass, which mostly group and osteopenia group [102] . They are likely to function
affects cancellous bone . Periodontitis involves local by working together, suggesting that these proteins in
[99]
inflammatory alveolar ridge loss, following an infectious exosomes affect the process of systemic bone changes.
Figure 3. The bridging role of exosomes between periodontitis and systemic diseases. The occurrence of periodontitis renders the body in an inflammatory
state, which can promote the secretion of exosomes by a variety of cells. Nucleic acid, protein, and lipid can be transmitted between various cells through
the exosomes, which can be used as messengers to mediate multiple cells signaling pathways, and then participate in the pathogenesis of osteoporosis, renal
fibrosis, AD, stroke, oral cancer, and cardiovascular disease.
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2022) 7 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.v1i2.99