Page 105 - GPD-2-1
P. 105
Gene & Protein in Disease SCN7A is a protective factor in LUAD
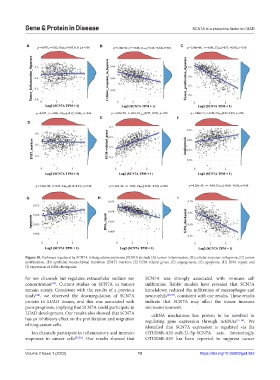
A B C
E F
D
G H I
Figure 10. Pathways regulated by SCN7A in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) include (A) tumor inflammation, (B) cellular response to hypoxia, (C) tumor
proliferation, (D) epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers, (E) ECM-related genes, (F) angiogenesis, (G) apoptosis, (H) DNA repair, and
(I) expression of G2M checkpoint.
for ion channels but regulates extracellular sodium ion SCN7A was strongly associated with immune cell
concentration . Current studies on SCN7A in tumors infiltration. Rabbit models have revealed that SCN7A
[26]
remain scanty. Consistent with the results of a previous knockdown reduced the infiltration of macrophages and
study , we observed the downregulation of SCN7A neutrophils [29,30] , consistent with our results. These results
[24]
protein in LUAD tissues, and this was associated with indicate that SCN7A may affect the tumor immune
poor prognosis, implying that SCN7A could participate in microenvironment.
LUAD development. Our results also showed that SCN7A ceRNA mechanism has proven to be involved in
has an inhibitory effect on the proliferation and migration regulating gene expression through ncRNAs [31-34] . We
of lung cancer cells. identified that SCN7A expression is regulated via the
Ion channels participate in inflammatory and immune OTUD6B-AS1-miR-21-5p-SCN7A axis. Interestingly,
responses in cancer cells [27,28] . Our results showed that OTUD6B-AS1 has been reported to suppress cancer
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2023) 10 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.363