Page 104 - GPD-2-1
P. 104
Gene & Protein in Disease SCN7A is a protective factor in LUAD
A B
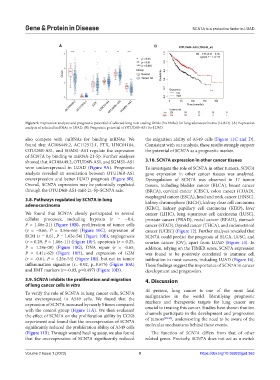
Figure 9. Expression analysis and prognostic potential of selected long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) for lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). (A) Expression
analysis of selected lncRNAs in LUAD. (B) Prognostic potential of OTUD6B-AS1 for LUAD.
also compete with miRNAs for binding mRNAs. We the migration ability of A549 cells (Figure 11C and D).
found that AC108449.2, AC112512.1, FTX, LINC01184, Consistent with our analysis, these results strongly support
OTUD6B-AS1, and SGMS1-AS1 regulate the expression the potential of SCN7A as a prognostic marker.
of SCN7A by binding to miRNA-21-5p. Further analyses
showed that AC108449.2, OTUD6B-AS1, and SGMS1-AS1 3.10. SCN7A expression in other cancer tissues
were underexpressed in LUAD (Figure 9A). Prognostic To investigate the role of SCN7A in other tumors, SCN7A
analysis revealed an association between OTUD6B-AS1 gene expression in other cancer tissues was analyzed.
overexpression and better LUAD prognosis (Figure 9B). Dysregulation of SCN7A was observed in 17 tumor
Overall, SCN7A expression may be potentially regulated tissues, including bladder cancer (BLCA), breast cancer
through the OTUD6B-AS1-miR-21-5p-SCN7A axis. (BRCA), cervical cancer (CESC), colon cancer (COAD),
esophageal cancer (ESCA), head and neck cancer (HNSC),
3.8. Pathways regulated by SCN7A in lung kidney chromophore (KICH), kidney clear cell carcinoma
adenocarcinoma
(KIRC), kidney papillary cell carcinoma (KIRP), liver
We found that SCN7A closely participated in several cancer (LIHC), lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC),
cellular processes, including hypoxia (r = −0.4, prostate cancer (PRAD), rectal cancer (READ), stomach
P = 1.06e-21) (Figure 10B), proliferation of tumor cells cancer (STAD), thyroid cancer (THCA), and endometrioid
(r = −0.66, P = 3.56e-66) (Figure 10C), expression of cancer (UCEC) (Figure 12). Further analyses revealed that
ECM (r = 0.61, P = 1.63e-54) (Figure 10E), angiogenesis SCN7A could predict the prognosis of BLCA, LUSC, and
(r = 0.29, P = 1.06e-11) (Figure 10F), apoptosis (r = 0.25, ovarian cancer (OV), apart from LUAD (Figure 13). In
P = 1.24e-08) (Figure 10G), DNA repair (r = -0.65, addition, relying on the TIMER score, SCN7A expression
P = 1.41e-62) (Figure 10H), and expression of G2M was found to be positively correlated to immune cell
(r = -0.61, P = 4.25e-54) (Figure 10I). but not in tumor infiltration in most cancers, including LUAD (Figure 14).
inflammation signature (r=-0.02, p=0.675) (Figure 10A) These findings suggest the importance of SCN7A in cancer
and EMT markers (r=-0.03, p=0.497) (Figure 10D). development and progression.
3.9. SCN7A inhibits the proliferation and migration 4. Discussion
of lung cancer cells in vitro
To verify the role of SCN7A in lung cancer cells, SCN7A At present, lung cancer is one of the most fatal
was overexpressed in A549 cells. We found that the malignancies in the world. Identifying prognostic
expression of SCN7A increased by nearly 5 times compared markers and therapeutic targets for lung cancer are
with the control group (Figure 11A). We then evaluated crucial to treating this cancer. Studies have shown that ion
channels participate in the development and progression
the effect of SCN7A on the proliferation ability by CCK8 of tumors [22-25] , underscoring the need to be aware of the
experiment and found that the overexpression of SCN7A
significantly reduced the proliferation ability of A549 cells molecular mechanisms behind these events.
(Figure 11B). Through wound healing assay, we also found The function of SCN7A differs from that of other
that the overexpression of SCN7A significantly reduced related genes. Precisely, SCN7A does not act as a switch
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2023) 9 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.363