Page 76 - GPD-2-1
P. 76
Gene & Protein in Disease m1A-mediated ESCCAL-1 promotes ESCA stemness
A B E
C D F
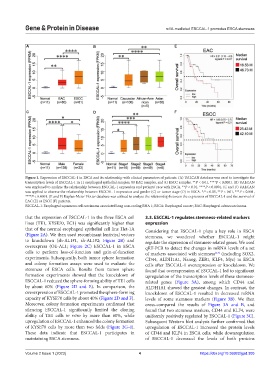
Figure 1. Expression of ESCCAL-1 in ESCA and its relationship with clinical parameters of patients. (A) UALCAN database was used to investigate the
transcription levels of ESCCAL-1 in 11 esophageal epithelial samples, 80 EAC samples, and 81 ESCC samples. **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001. (B) UALCAN
was employed to analyze the relationship between ESCCAL-1 expression and patients’ race with ESCA. **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001. (C and D) UALCAN
was applied to observe the relationship between ESCCAL-1 expression and gender (C) or tumor stage (D) in ESCA. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001,
****P < 0.0001. (E and F) Kaplan-Meier Plotter database was utilized to analyze the relationship between the expression of ESCCAL-1 and the survival of
EAC (E) or ESCC (F) patients.
ESCCAL-1: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma associated long non-coding RNA 1; ESCA: Esophageal cancer; EAC: Esophageal adenocarcinoma.
that the expression of ESCCAL-1 in the three ESCA cell 3.3. ESCCAL-1 regulates stemness-related markers
lines (TE1, KYSE70, EC1) was significantly higher than expression
that of the normal esophageal epithelial cell line Het-1A Considering that ESCCAL-1 plays a key role in ESCA
(Figure 2A). We then used recombinant lentiviral vectors stemness, we wondered whether ESCCAL-1 might
to knockdown (sh-AL1#1, sh-AL1#2; Figure 2B) and regulate the expression of stemness-related genes. We used
overexpress (OE-AL1; Figure 2C) ESCCAL-1 in ESCA qRT-PCR to detect the changes in mRNA levels of a set
cells to perform loss-of-function and gain-of-function of markers associated with stemness (including SOX2,
[17]
experiments. Subsequently, both tumor sphere formation CD44, ALDH1A1, Nanog, ZEB1, KLF4, Myc) in ESCA
and colony formation assays were used to evaluate the cells after ESCCAL-1 overexpression or knockdown. We
stemness of ESCA cells. Results from tumor sphere found that overexpression of ESCCAL-1 led to significant
formation experiments showed that the knockdown of upregulation of the transcription levels of these stemness-
ESCCAL-1 reduced the sphere-forming ability of TE1 cells related genes (Figure 3A), among which CD44 and
by about 60% (Figure 2D and E). In comparison, the ALDH1A1 showed the greatest changes. In contrast, the
overexpression of ESCCAL-1 promoted the sphere-forming knockdown of ESCCAL-1 resulted in decreased mRNA
capacity of KYSE70 cells by about 40% (Figure 2D and F). levels of some stemness markers (Figure 3B). We then
Moreover, colony formation experiments confirmed that cross-compared the results of Figure 3A and B, and
silencing ESCCAL-1 significantly limited the cloning found that two stemness markers, CD44 and KLF4, were
ability of TE1 cells in vitro by more than 60%, while uniformly positively regulated by ESCCAL-1 (Figure 3C).
upregulation of ESCCAL-1 enhanced the colony formation Subsequent Western blot analysis further confirmed that
of KYSE70 cells by more than two folds (Figure 2G–I). upregulation of ESCCAL-1 increased the protein levels
These data indicate that ESCCAL-1 participates in of CD44 and KLF4 in ESCA cells, while downregulation
maintaining ESCA stemness. of ESCCAL-1 decreased the levels of both proteins
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2023) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.305