Page 78 - GPD-2-1
P. 78
Gene & Protein in Disease m1A-mediated ESCCAL-1 promotes ESCA stemness
A C
B D
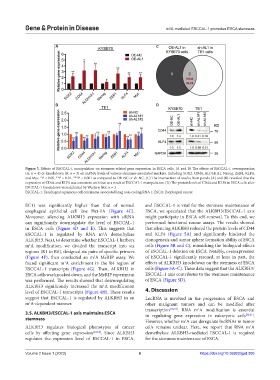
Figure 3. Effects of ESCCAL-1 manipulation on stemness-related gene expression in ESCA cells. (A and B) The effects of ESCCAL-1 overexpression
(A, n = 4) or knockdown (B, n = 3) on mRNA levels of various stemness-associated markers, including SOX2, CD44, ALDH1A1, Nanog, ZEB1, KLF4,
and Myc. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 as compared to OE-NC or sh-NC. (C) The intersection of results from panels (A) and (B) revealed that the
expression of CD44 and KLF4 was consistent with that as a result of ESCCAL-1 manipulation. (D) The protein levels of CD44 and KLF4 in ESCA cells after
ESCCAL-1 knockdown were detected by Western blot, n = 3.
ESCCAL-1: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma associated long non-coding RNA 1; ESCA: Esophageal cancer.
EC1) was significantly higher than that of normal and ESCCAL-1 is vital for the stemness maintenance of
esophageal epithelial cell line Het-1A (Figure 4C). ESCA, we speculated that the ALKBH3/ESCCAL-1 axis
Moreover, silencing ALKBH3 expression with siRNA might participate in ESCA self-renewal. To this end, we
can significantly downregulate the level of ESCCAL-1 performed functional rescue assays. The results showed
in ESCA cells (Figure 4D and E). This suggests that that silencing ALKBH3 reduced the protein levels of CD44
ESCCAL-1 is regulated by RNA m A demethylase and KLF4 (Figure 5A) and significantly hindered the
1
ALKBH3. Next, to determine whether ESCCAL-1 harbors clonogenesis and tumor sphere formation ability of ESCA
1
m A modification, we divided the transcript into six cells (Figure 5B and C), mimicking the biological effects
regions (R1 to R6), designed six pairs of specific primers of ESCCAL-1 deletion on ESCA. Notably, overexpression
(Figure 4F), then conducted an m A MeRIP assay. We of ESCCAL-1 significantly rescued, at least in part, the
1
1
found significant m A enrichment in the R4 region of effects of ALKBH3 knockdown on the stemness of ESCA
ESCCAL-1 transcripts (Figure 4G). Then, ALKBH3 in cells (Figure 5A–C). These data suggest that the ALKBH3/
ESCA cells was knocked down, and the MeRIP experiment ESCCAL-1 axis contributes to the stemness maintenance
was performed. The results showed that downregulating of ESCA (Figure 5D).
1
ALKBH3 significantly increased the m A modification
level of ESCCAL-1 transcripts (Figure 4H). These results 4. Discussion
suggest that ESCCAL-1 is regulated by ALKBH3 in an LncRNA is involved in the progression of ESCA and
m A-dependent manner. other malignant tumors and can be modified after
1
transcription [18,19] . RNA m A modification is essential
1
3.5. ALKBH3/ESCCAL-1 axis maintains ESCA in regulating gene expression in eukaryotic cells [20,21] .
stemness However, whether m A can deregulate lncRNAs in tumor
1
ALKBH3 regulates biological phenotypes of cancer cells remains unclear. Here, we report that RNA m A
1
cells by affecting gene expression [13,14] . Since ALKBH3 demethylase ALKBH3-mediated ESCCAL-1 is required
regulates the expression level of ESCCAL-1 in ESCA, for the stemness maintenance of ESCA.
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2023) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.305