Page 39 - GPD-3-2
P. 39
Gene & Protein in Disease β-cell regeneration and stem cell niche
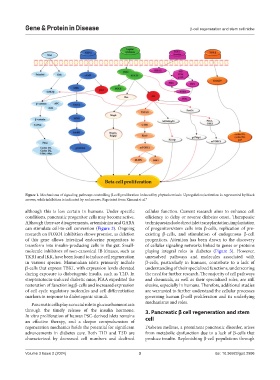
Figure 1. Mechanisms of signaling pathways controlling β-cell proliferation induced by phytochemicals. Upregulation/activation is represented by black
arrows, while inhibition is indicated by red arrows. Reprinted from Kimani et al. 9
although this is less certain in humans. Under specific cellular function. Current research aims to enhance cell
conditions, pancreatic progenitor cells may become active. efficiency to delay or reverse diabetes onset. Therapeutic
Although there are disagreements, artemisinins and GABA techniques include direct islet transplantation, implantation
can stimulate cell-to-cell conversion (Figure 2). Ongoing of progenitors/stem cells into β-cells, replication of pre-
research on FOXO1 inhibition shows promise, as deletion existing β-cells, and stimulation of endogenous β-cell
of this gene allows intestinal endocrine progenitors to progenitors. Attention has been drawn to the discovery
transform into insulin-producing cells in the gut. Small- of cellular signaling networks linked to genes or proteins
molecule inhibitors of non-canonical IB kinases, such as playing integral roles in diabetes (Figure 3). However,
TKB1 and IKK, have been found to induce cell regeneration unresolved pathways and molecules associated with
in various species. Mammalian islets primarily include β-cells, particularly in humans, contribute to a lack of
β-cells that express TBK1, with expression levels elevated understanding of their specialized functions, underscoring
during exposure to diabetogenic insults, such as T2D. In the need for further research. The majority of cell pathways
streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice, PIAA expedited the and chemicals, as well as their specialized roles, are still
restoration of functioning β-cells and increased expression elusive, especially in humans. Therefore, additional studies
of cell cycle regulatory molecules and cell differentiation are warranted to further understand the cellular processes
markers in response to diabetogenic stimuli. governing human β-cell proliferation and its underlying
mechanisms and roles.
Pancreatic cells play a crucial role in glucose homeostasis
through the timely release of the insulin hormone. 3. Pancreatic β cell regeneration and stem
In vitro proliferation of human PSC-derived islets remains cell
an effective therapy, and a deeper comprehension of
regeneration mechanics holds the potential for significant Diabetes mellitus, a prominent pancreatic disorder, arises
advancements in diabetes care. Both T1D and T2D are from metabolic dysfunction due to a lack of β-cells that
characterized by decreased cell numbers and declined produce insulin. Replenishing β-cell populations through
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 3 doi: 10.36922/gpd.2996