Page 41 - GPD-3-2
P. 41
Gene & Protein in Disease β-cell regeneration and stem cell niche
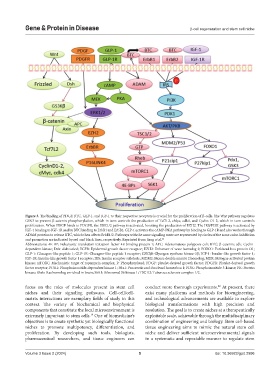
Figure 3. The binding of PDGF, BTC, GLP-1, and IGF-1 to their respective receptors is crucial for the proliferation of β-cells. The Wnt pathway regulates
GSK3 to prevent β-catenin phosphorylation, which in turn controls the production of Tcf7L2, cMyc, cdk4, and Cyclin D1-2, which in turn controls
proliferation. When PDGF binds to PDGFR, the ERK1/2 pathway is activated, boosting the production of EZH2. The IRS/PI3K pathway is activated by
IGF-1 binding to IGF-1R and by BTC binding to ErbB1 and ErbB2. GLP-1 activates the cAMP-PKA pathway by binding to GLP-1R and also works through
ADAM proteins to release BTC, which then affects ErbB1/2. Pathways with the same signaling route are represented by circles of the same color. Inhibition
and promotion are indicated by red and black lines, respectively. Reprinted from Jiang et al. 11
Abbreviations: 4E-BP: Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1; APC: Adenomatous polyposis coli; BTC: β-catenin; cdk: Cyclin-
dependent kinase; Dsh: disheveled; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; EZH2: Enhancer of zeste homolog 2; FOXO1: Forkhead box protein O1;
GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide 1; GLP-1R: Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor; GSK3β: Glycogen synthase kinase-3β; IGF-1: Insulin-like growth factor 1;
IGF-1R: Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor; IRS: Insulin receptor substrate; MDM2: Mouse double minute 2 homolog; MEK: Mitogen-activated protein
kinase; mTORC: Mechanistic target of rapamycin complex; P: Phosphorylated; PDGF: platelet-derived growth factor; PDGFR: Platelet-derived growth
factor receptor; PDK1: Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1; Pdx1: Pancreatic and duodenal homeobox 1; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PK: Protein
kinase; Rheb: Ras homolog enriched in brain; S6K1: Ribosomal S6 kinase 1; TSC1/2: Tuberous sclerosis complex 1/2.
focus on the roles of molecules present in stem cell conduct more thorough experiments. At present, there
20
niches and their signaling pathways. Cell-cell/cell- exist many platforms and methods for bioengineering,
matrix interactions are exemplary fields of study in this and technological advancements are available to explore
context. The variety of biochemical and biophysical biological transformations with high precision and
components that constitute the local microenvironment is resolution. The goal is to create niches at a therapeutically
extremely important to stem cells. One of biomedicine’s exploitable scale, achievable through the multidisciplinary
19
objectives is to create synthetic yet biologically functional combination of engineering and biology. Stem cell-based
niches to promote multipotency, differentiation, and tissue engineering aims to mimic the natural stem cell
proliferation. By developing such tools, biologists, niche and deliver sufficient microenvironmental signals
pharmaceutical researchers, and tissue engineers can in a systematic and repeatable manner to regulate stem
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 5 doi: 10.36922/gpd.2996