Page 40 - GPD-3-2
P. 40
Gene & Protein in Disease β-cell regeneration and stem cell niche
abundant source of healthy β-cells. Glucose, through
unfolded proteins and metabolic pathways, significantly
influences quiescent β-cells’ entry into the cell cycle.
15
Hormones, growth factors, and signaling pathways,
including the calcium-calcineurin nuclear factor of
activated T lymphocytes, exert varying impacts on
β-cell replication. Therefore, a deeper comprehension
of the molecular mechanisms underpinning pancreatic
β-cell regeneration and protection holds promise for the
discovery and development of novel therapeutic strategies.
The integration of stem cells and diverse phytochemicals
has opened up new avenues for arresting β-cell senescence
and fostering islet regeneration. Given that diabetes results
from insufficient pancreatic β-cell mass, the replacement
of functional β-cells stands out as a promising treatment
(Figure 4).
To increase β-cell mass, stimulating the replication of
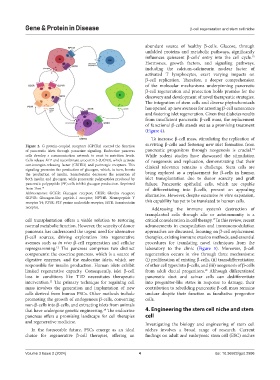
Figure 2. G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) control the function surviving β-cells and fostering new islet formation from
14
of pancreatic islets through paracrine signaling. Endocrine pancreas pancreatic progenitors through neogenesis is crucial.
cells develop a communication network to react to nutrition levels. While rodent studies have showcased the stimulation
Cells release ATP and recombinant urocortin 3 (UCN3), which activate of neogenesis and replication, demonstrating that their
corticotropin-releasing factor (CRHR2) and purinergic receptors. This clinical relevance remains a challenge. Stem cells are
signaling promotes the production of glucagon, which, in turn, boosts
the production of insulin. Somatostatin decreases the secretion of being explored as a replacement for β-cells in human
both insulin and glucagon, while pancreatic polypeptides produced by islet transplantation due to donor scarcity and graft
pancreatic polypeptide (PP) cells inhibit glucagon production. Reprinted failure. Pancreatic epithelial cells, which are capable
from Thor. 10 of differentiating into β-cells, present an appealing
Abbreviations: GCGR: Glucagon receptor; GHSR: Ghrelin receptor; alternative. However, despite extensive in vitro expansion,
GLP1R: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor; NPY4R: Neuropeptide Y
receptor Y4; P2YR: P2Y purine nucleotide receptor; SSTR: Somatostatin this capability has yet to be translated to human cells.
receptor. Addressing the immune system’s destruction of
transplanted cells through allo or autoimmunity is a
cell transplantation offers a viable solution to restoring critical consideration in cell therapy. In this review, recent
17
normal metabolic function. However, the scarcity of donor advancements in encapsulation and immunomodulation
pancreata has underscored the urgent need for alternative approaches are discussed, focusing on β-cell replacement
β-cell sources, driving exploration into regenerative therapies, existing immune evasion methods, and essential
avenues such as in vivo β-cell regeneration and cellular procedures for translating novel techniques from the
reprogramming. The pancreas comprises two distinct laboratory to the clinic (Figure 5). Moreover, β-cell
12
components: the exocrine pancreas, which is a source of regeneration occurs in vivo through three mechanisms:
digestive enzymes, and the endocrine islets, which are (i) proliferation of existing β-cells, (ii) transdifferentiation
responsible for insulin production. Human islets exhibit of other cell types into β-cells, and (iii) neogenesis of β-cells
limited regenerative capacity. Consequently, islet β-cell from adult ductal progenitors. Although differentiated
18
loss in conditions like T1D necessitates therapeutic pancreatic duct and acinar cells can dedifferentiate
intervention. The primary technique for regaining cell into progenitor-like states in response to damage, their
13
mass involves the generation and implantation of new contribution to rebuilding pancreatic β-cell mass remains
cells derived from human PSCs. Other methods include unclear despite their function as facultative progenitor
promoting the growth of endogenous β-cells, converting cells.
non-β-cells into β-cells, and extracting islets from animals
that have undergone genetic engineering. The endocrine 4. Engineering the stem cell niche and stem
14
pancreas offers a promising landscape for cell therapies cell
and regenerative medicine. Investigating the biology and engineering of stem cell
In the foreseeable future, PSCs emerge as an ideal niches involves a broad range of research. Current
choice for regenerative β-cell therapies, offering an findings on adult and embryonic stem cell (ESC) niches
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 4 doi: 10.36922/gpd.2996