Page 42 - GPD-3-2
P. 42
Gene & Protein in Disease β-cell regeneration and stem cell niche
engineering and regeneration. In coculture settings, stem
cells exhibit the ability to support tissue homeostasis,
repair, metabolism, and growth, while also serving as
targets for differentiation into various cell types. The
26
development of complex tissues or organs hinges on
their integration into coculture systems, employing both
direct and indirect coculture approaches to elucidate
cellular events in tissue engineering. This review
27
discusses the benefits of stem cell co-culture techniques
in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, with a
particular focus on various tissues, including orthopedic
soft tissues, vasculature, bone, heart, lung, nerve, kidney,
and liver. Despite recent exciting discoveries, a decade
of experimental and clinical studies has shown that the
routine use of stem cells to repair solid organs is not
imminent amidst the promise of their medicinal uses in
cell-based tissue regeneration, drug testing, and basic
28
research. Biologists only partially comprehend the
mechanisms governing cell differentiation, with only
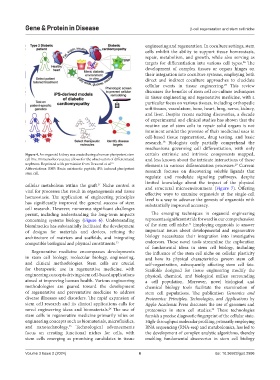
Figure 4. An organoid kidney was created using a human pluripotent stem certain extrinsic and intrinsic components mapped,
cell line. Immunofluorescence allows for the observation of differentiated and less known about the intricate interactions of these
nephrons. Reprinted with permission from Drawnel et al. 16 elements in various differentiation processes. Current
29
Abbreviations: BNP: Brain natriuretic peptide; iPS: induced pluripotent research focuses on discovering soluble ligands that
stem cell.
regulate and modulate signaling pathways, despite
limited knowledge about the impact of the physical
cellular metabolism within the graft. Niche control is and structural microenvironment (Figure 7). Offering
21
vital for processes that result in organogenesis and tissue effective ways to examine organoids at the single-cell
homeostasis. The application of engineering principles level is a way to advance the genesis of organoids with
has significantly improved the general success of stem substantially improved accuracy.
cell research. However, numerous significant challenges
persist, including understanding the long-term impacts The emerging techniques in organoid engineering
concerning systems biology (Figure 6). Understanding represent a significant stride forward in our comprehension
31
biomimetics has substantially facilitated the development of the stem cell niche. Employing organoids to answer
of designs for materials and devices, refining the important issues about developmental and regenerative
architecture of matrices and scaffolds, and integrating biology necessitates their integration into investigative
compatible biological and physical constituents. 22 endeavors. These novel tools streamline the exploration
of fundamental ideas in stem cell biology, including
Regenerative medicine encompasses developments the influence of the stem cell niche on cellular plasticity
in stem cell biology, molecular biology, engineering, and how its physical characteristics govern stem cell
and clinical methodologies. Stem cells are crucial self-organization, subsequently affecting stem cell fate.
for therapeutic use in regenerative medicine, with Scaffolds designed for tissue engineering modify the
engineering concepts driving stem cell-based applications physical, chemical, and biological milieu surrounding
aimed at improving human health. Various engineering a cell population. Moreover, novel biological and
methodologies are geared toward the development chemical biology tools facilitate the examination of
of regenerative and preventative medicine to address stem cell populations. The publication Genomics and
diverse illnesses and disorders. The rapid expansion of Proteomics: Principles, Technologies, and Applications by
stem cell research and its clinical applications calls for Apple Academic Press discusses the use of genomes and
novel engineering ideas and biomaterials. The use of proteomics in stem cell studies. These technologies
24
32
stem cells in regenerative medicine primarily relies on furnish a precise diagnostic fingerprint of the cellular state.
engineering concepts such as biomaterials, microfluidics, High-throughput molecular profiling, primarily employing
and nanotechnology. Technological advancements RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) and metabolomics, has led to
25
focus on creating functional niches for cells, with the development of complex analytic algorithms, thereby
stem cells emerging as promising candidates in tissue enabling fundamental discoveries in stem cell biology
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 6 doi: 10.36922/gpd.2996