Page 45 - GPD-3-2
P. 45
Gene & Protein in Disease β-cell regeneration and stem cell niche
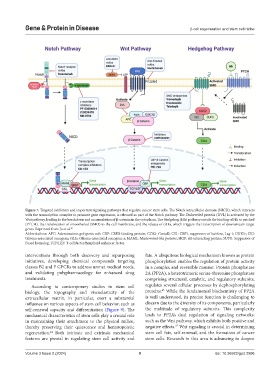
Figure 7. Targeted inhibitors and important signaling pathways that regulate cancer stem cells. The Notch intracellular domain (NICD), which interacts
with the transcription complex to promote gene expression, is released as part of the Notch pathway. The Dishevelled protein (DVL) is activated by the
Wnt pathway, leading to the breakdown and accumulation of β-catenin in the cytoplasm. The Hedgehog (Hh) pathway entails the binding of Hh to patched
(PTCH), the translocation of smoothened (SMO) to the cell membrane, and the release of GLIa, which triggers the transcription of downstream target
genes. Reprinted from Ju et al. 30
Abbreviations: APC: Adenomatous polyposis coli; CBP: CREB-binding protein; COS2: Costal2; CSL: CBF1, suppressor of hairless, Lag-1; DKK1:; GLI:
Glioma-associated oncogene; GLIa: Glioma-associated oncogene a; MAML: Mastermind-like proteins; SKIP: ski-interacting protein; SUFU: Suppressor of
Fused homolog; TCF/LEF: T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor.
interventions through both discovery and repurposing fate. A ubiquitous biological mechanism known as protein
initiatives, developing chemical compounds targeting phosphorylation enables the regulation of protein activity
classes B2 and F GPCRs to address unmet medical needs, in a complex and reversible manner. Protein phosphatase
and validating polypharmacology for enhanced drug 2A (PP2A), a heterotrimeric serine-threonine phosphatase
treatments. comprising structural, catalytic, and regulatory subunits,
According to contemporary studies in stem cell regulates several cellular processes by dephosphorylating
45
biology, the topography and viscoelasticity of the proteins. While the fundamental biochemistry of PP2A
extracellular matrix, in particular, exert a substantial is well understood, its precise function is challenging to
influence on various aspects of stem cell behavior, such as discern due to the diversity of its components, particularly
self-renewal capacity and differentiation (Figure 9). The the multitude of regulatory subunits. This complexity
mechanical characteristics of stem cells play a crucial role leads to PP2A’s dual regulation of signaling networks,
in maintaining their attachment to the physical milieu, such as the Wnt pathway, which exhibits both positive and
27
thereby preserving their quiescence and hematopoietic negative effects. Wnt signaling is crucial in determining
regeneration. Both intrinsic and extrinsic mechanical stem cell fate, self-renewal, and the formation of cancer
44
features are pivotal in regulating stem cell activity and stem cells. Research in this area is advancing to deepen
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 9 doi: 10.36922/gpd.2996