Page 116 - GPD-3-4
P. 116
Gene & Protein in Disease Pre-metastatic niche oral cancer: Insights
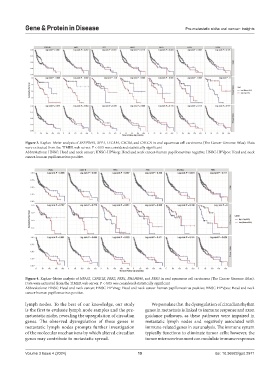
Figure 3. Kaplan–Meier analysis of SERPINE1, SPP1, L1CAM, CXCR4, and CALCA in oral squamous cell carcinoma (The Cancer Genome Atlas). Data
were extracted from the TIMER web server. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant
Abbreviations: HNSC: Head and neck cancer; HNSC-HPVneg: Head and neck cancer-human papillomavirus negative; HNSC-HPVpos: Head and neck
cancer-human papillomavirus positive.
Figure 4. Kaplan–Meier analysis of NPAS2, CSNK1E, PER2, PER1, BHLHE40, and PER3 in oral squamous cell carcinoma (The Cancer Genome Atlas).
Data were extracted from the TIMER web server. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant
Abbreviations: HNSC: Head and neck cancer; HNSC-HPVneg: Head and neck cancer-human papillomavirus positive; HNSC-HPVpos: Head and neck
cancer-human papillomavirus positive.
lymph nodes. To the best of our knowledge, our study We postulate that the dysregulation of circadian rhythm
is the first to evaluate lymph node samples and the pre- genes in metastasis is linked to immune response and axon
metastatic niche, revealing the upregulation of circadian guidance pathways, as these pathways were impaired in
genes. The observed dysregulation of these genes in metastatic lymph nodes and negatively associated with
metastatic lymph nodes prompts further investigation immune-related genes in our analysis. The immune system
of the molecular mechanisms by which altered circadian typically functions to eliminate tumor cells; however, the
genes may contribute to metastatic spread. tumor microenvironment can modulate immune responses
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 19 doi: 10.36922/gpd.2971