Page 141 - GPD-3-4
P. 141
Gene & Protein in Disease A pyroptosis-related gene signature in myeloma
A B
C D
E F
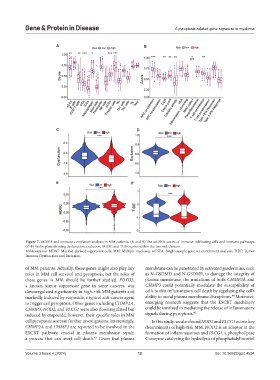
Figure 7. ssGSEA and immune correlation analysis in MM patients. (A and B) The ssGSEA scores of immune-infiltrating cells and immune pathways.
(C-F) Violin plots showing dysfunction, exclusion, MDSC and TIDE scores within the two risk clusters.
Abbreviations: MDSC: Myeloid-derived suppressor cells; MM: Multiple myeloma; ssGSEA: Single-sample gene set enrichment analysis; TIDE: Tumor
Immune Dysfunction and Exclusion.
of MM patients. Actually, these genes might also play key membrane can be penetrated by activated gasdermins, such
roles in MM cell survival and pyroptosis, but the roles of as N-GSDMD and N-GSDME, to damage the integrity of
these genes in MM should be further studied. FOXO3, plasma membrane, the mutations of both CHMP2A and
a known tumor suppressor gene in some cancers, was CHMP3 could potentially modulate the susceptibility of
downregulated significantly in high-risk MM patients and cells to this inflammatory cell death by regulating the cell’s
44
markedly induced by etoposide, a typical anti-cancer agent ability to mend plasma membrane disruptions. Moreover,
to trigger cell pyroptosis. Other genes including CHMP2A, emerging research suggests that the ESCRT machinery
CHMP3, NOD2, and PLCG1 were also downregulated but could be involved in mediating the release of inflammatory
induced by etoposide; however, their specific roles in MM signals during pyroptosis. 45
cell pyroptosis warrant further investigations. Interestingly, In this study, we also found NOD2 and PLCG1 as two key
CHMP2A and CHMP3 are reported to be involved in the determinants of high-risk MM. NOD2 is an adaptor in the
ESCRT pathway, crucial in plasma membrane repair, formation of inflammasomes and PLCG1, a phospholipase
a process that can avert cell death. Given that plasma C enzyme catalyzing the hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol
43
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 12 doi: 10.36922/gpd.4534