Page 140 - GPD-3-4
P. 140
Gene & Protein in Disease A pyroptosis-related gene signature in myeloma
A B
C
D
E F
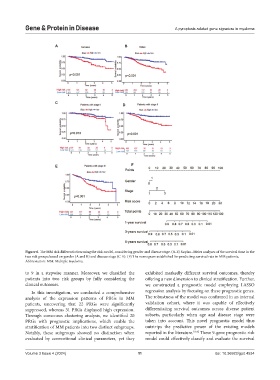
Figure 6. The MM risk differentiation using the risk model, considering gender and disease stage. (A-E) Kaplan–Meier analyses of the survival time in the
two risk groups based on gender (A and B) and disease stage (C-E). (F) The nomogram established for predicting survival rate in MM patients.
Abbreviation: MM: Multiple myeloma.
to 9 in a stepwise manner. Moreover, we classified the exhibited markedly different survival outcomes, thereby
patients into two risk groups by fully considering the offering a new dimension to clinical stratification. Further,
clinical outcomes. we constructed a prognostic model employing LASSO
In this investigation, we conducted a comprehensive regression analysis by focusing on these prognostic genes.
analysis of the expression patterns of PRGs in MM The robustness of the model was confirmed in an internal
patients, uncovering that 22 PRGs were significantly validation cohort, where it was capable of effectively
suppressed, whereas 31 PRGs displayed high expression. differentiating survival outcomes across diverse patient
Through consensus clustering analysis, we identified 20 subsets, particularly when age and disease stage were
PRGs with prognostic implications, which enable the taken into account. This novel prognostic model thus
stratification of MM patients into two distinct subgroups. outstrips the predictive power of the existing models
Notably, these subgroups showed no distinction when reported in the literature. 18,42 These 9-gene prognostic risk
evaluated by conventional clinical parameters, yet they model could effectively classify and evaluate the survival
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 11 doi: 10.36922/gpd.4534