Page 135 - GPD-3-4
P. 135
Gene & Protein in Disease A pyroptosis-related gene signature in myeloma
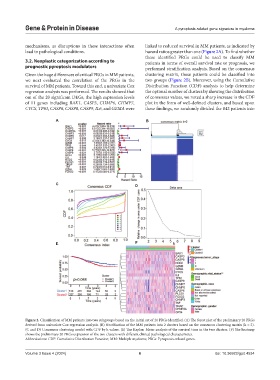
mechanisms, as disruptions in these interactions often linked to reduced survival in MM patients, as indicated by
lead to pathological conditions. hazard ratios greater than one (Figure 2A). To find whether
these identified PRGs could be used to classify MM
3.2. Neoplastic categorization according to patients in terms of overall survival rate or prognosis, we
prognostic pyroptosis modulators performed stratification analysis. Based on the consensus
Given the huge differences of critical PRGs in MM patients, clustering matrix, these patients could be classified into
we next evaluated the correlation of the PRGs in the two groups (Figure 2B). Moreover, using the Cumulative
survival of MM patients. Toward this end, a univariate Cox Distribution Function (CDF) analysis to help determine
regression analysis was performed. The results showed that the optimal number of clusters by showing the distribution
out of the 20 significant DEGs, the high expression levels of consensus values, we noted a sharp increase in the CDF
of 11 genes including BAK1, CASP3, CHMP6, CHMP7, plot in the form of well-defined clusters, and based upon
CYCS, TP63, CASP6, CASP8, CASP9, IL6, and GZMA were these findings, we randomly divided the 842 patients into
A B
C D
E F
Figure 2. Classification of MM patients into two subgroups based on the initial set of 20 PRGs identified. (A) The forest plot of the preliminary 20 PRGs
derived from univariate Cox regression analysis. (B) Stratification of the MM patients into 2 clusters based on the consensus clustering matrix (k = 2).
(C and D) Consensus clustering model with CDF by k values. (E) The Kaplan–Meier analysis of the survival time in the two clusters. (F) The heatmap
shows the preliminary 20 PRGs expression of the two clusters with different clinical pathological characteristics.
Abbreviations: CDF: Cumulative Distribution Function; MM: Multiple myeloma; PRGs: Pyroptosis-related genes.
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 6 doi: 10.36922/gpd.4534