Page 139 - GPD-3-4
P. 139
Gene & Protein in Disease A pyroptosis-related gene signature in myeloma
A B
C D
E F
G H
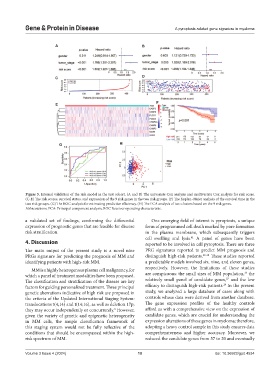
Figure 5. Internal validation of the risk model in the test cohort. (A and B) The univariate Cox analysis and multivariate Cox analysis for risk score.
(C-E) The risk scores, survival status, and expression of the 9 risk genes in the two risk groups. (F) The Kaplan–Meier analysis of the survival time in the
two risk groups. (G) The ROC analysis for estimating predictive efficiency. (H) The PCA analysis of two clusters based on the 9 risk genes.
Abbreviations: PCA: Principal component analysis; ROC Receiver operating characteristic.
a validated set of findings, confirming the differential One emerging field of interest is pyroptosis, a unique
expression of prognostic genes that are feasible for disease form of programmed cell death marked by pore formation
risk stratification. in the plasma membrane, which subsequently triggers
cell swelling and lysis. A panel of genes have been
41
4. Discussion reported to be involved in cell pyroptosis. There are three
The main output of the present study is a novel nine PRG signatures reported to predict MM prognosis and
PRGs signature for predicting the prognosis of MM and distinguish high-risk patients. 26-28 These studies reported
identifying patients with high-risk MM. a predictable models involved six, nine, and eleven genes,
MM is a highly heterogenous plasma cell malignancy, for respectively. However, the limitations of these studies
26
which a panel of treatment modalities have been proposed. are conspicuous: the small sizes of MM population, the
27
The classification and stratification of the disease are key relatively small panel of candidate genes, and the low
28
factors for guiding personalized treatment. Three principal efficacy to distinguish high-risk patients. In the present
genetic aberrations indicative of high risk are proposed in study, we analyzed a large database of cases along with
the criteria of the Updated International Staging System: controls whose data were derived from another database.
translocations t(4;14) and t(14;16), as well as deletion 17p; The gene expression profiles of the healthy controls
they may occur independently or concurrently. However, afford us with a comprehensive view on the expression of
9
given the variety of genetic and epigenetic heterogeneity candidate genes, which are crucial for understanding the
in MM cells, the simple classification framework of expression alterations of these genes in myeloma; therefore,
this staging system would not be fully reflective of the adopting a heavy control sample in this study ensures data
conditions that should be encompassed within the high- comprehensiveness and higher accuracy. Moreover, we
risk spectrum of MM. reduced the candidate genes from 57 to 20 and eventually
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 10 doi: 10.36922/gpd.4534