Page 138 - GPD-3-4
P. 138
Gene & Protein in Disease A pyroptosis-related gene signature in myeloma
A B
C
D E
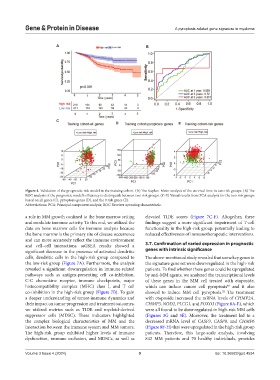
Figure 4. Validation of the prognostic risk model in the training cohort. (A) The Kaplan–Meier analysis of the survival time in two risk groups. (B) The
ROC analysis of the prognostic model’s efficiency to distinguish between two risk groups. (C-E) Visual results from PCA analysis for the two risk groups
based on all genes (C), pyroptosis genes (D), and the 9 risk genes (E).
Abbreviations: PCA: Principal component analysis; ROC Receiver operating characteristic.
a role in MM growth confined to the bone marrow setting elevated TIDE scores (Figure 7C-F). Altogether, these
and modulate immune activity. To this end, we utilized the findings suggest a more significant impairment of T-cell
data on bone marrow cells for immune analysis because functionality in the high-risk group, potentially leading to
the bone marrow is the primary site of disease occurrence reduced effectiveness of immunotherapeutic interventions.
and can more accurately reflect the immune environment
and cell–cell interactions. ssGSEA results showed a 3.7. Confirmation of varied expression in prognostic
significant decrease in the presence of activated dendritic genes with intrinsic significance
cells, dendritic cells in the high-risk group compared to The above-mentioned study revealed that some key genes in
the low-risk group (Figure 7A). Furthermore, the analysis the signature gene set were downregulated in the high-risk
revealed a significant downregulation in immune-related patients. To find whether these genes could be upregulated
pathways such as antigen-presenting cell co-inhibition, by anti-MM agents, we analyzed the transcriptional levels
C-C chemokine receptor, immune checkpoints, major of these genes in the MM cell treated with etoposide,
histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I, and T cell which can induce cancer cell pyroptosis and it also
40
co-inhibition in the high-risk group (Figure 7B). To gain showed to induce MM cell pyroptosis. The treatment
22
a deeper understanding of tumor-immune dynamics and with etoposide increased the mRNA levels of CHMP2A,
their impact on tumor progression and treatment outcomes, CHMP3, NOD2, PLCG1, and FOXO3 (Figure 8A-E), which
we utilized metrics such as TIDE and myeloid-derived were all found to be downregulated in high-risk MM cells
suppressor cells (MDSC). These indicators highlighted (Figures 3G and 5E). Moreover, the treatment led to a
the complex biological characteristics of MM and the decreased mRNA level of CASP3, CASP8, and CHMP6
interaction between the immune system and MM tumors. (Figure 8F-H) that were upregulated in the high-risk group
The high-risk group exhibited higher levels of immune patients. Therefore, this large-scale analysis, involving
dysfunction, immune exclusion, and MDSCs, as well as 842 MM patients and 70 healthy individuals, provides
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 9 doi: 10.36922/gpd.4534