Page 69 - GPD-3-4
P. 69
Gene & Protein in Disease Drugs and immune infiltration in IPF
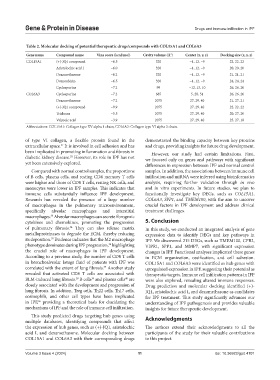
Table 2. Molecular docking of potential therapeutic drugs/compounds with COL15A1 and COL6A3
Gene name Compound name Vina score (kcal/mol) Cavity volume (Å ) Center (x, y, z) Docking size (x, y, z)
3
COL15A1 (+)-JQ1 compound −6.5 320 −1, 12, −9 22, 22, 22
Aristolochic acid I −6.0 320 −1, 12, −9 20, 20, 20
Dexamethasone −6.2 320 −1, 12, −9 21, 21, 21
Doxorubicin −6.5 320 −1, 12, −9 24, 24, 24
Cyclosporine −7.2 99 −12, 13, 10 26, 26, 26
COL6A3 Cyclosporine −7.2 685 5, 28, 51 26, 26, 26
Dexamethasone −7.2 2075 27, 29, 40 21, 27, 21
(+)-JQ1 compound −9.9 2075 27, 29, 40 22, 22, 22
Triclosan −5.5 2075 27, 29, 40 20, 27, 20
Valproic acid −3.9 2075 27, 29, 40 25, 27, 18
Abbreviations: COL15A1: Collagen type XV alpha 1 chain; COL6A3: Collagen type VI alpha 3 chain.
of type VI collagen, a flexible protein found in the demonstrated the binding capacity between key proteins
extracellular space. It is involved in cell adhesion and has and drugs, providing insights for future drug development.
31
been implicated in promoting inflammation and fibrosis in However, our study had certain limitations. First,
32
diabetic kidney disease. However, its role in IPF has not we focused only on genes and pathways with significant
yet been extensively explored. differences in expression between IPF and normal control
Compared with normal control samples, the proportions samples. In addition, the associations between immune cell
of B cells, plasma cells, and resting CD4 memory T cells infiltration and miRNA were inferred using bioinformatics
were higher and those of CD8 T cells, resting NK cells, and analysis, requiring further validation through in vivo
monocytes were lower in IPF samples. This indicates that and in vitro experiments. In future studies, we plan to
immune cells substantially influence IPF development. functionally investigate key DEGs, such as COL15A1,
Research has revealed the presence of a large number COL6A3, SPP1, and TMEM100, with the aim to uncover
of macrophages in the pulmonary microenvironment, crucial factors in IPF development and address clinical
specifically alveolar macrophages and interstitial treatment challenges.
macrophages. Alveolar macrophages can secrete fibrogenic
33
cytokines and chemokines, promoting the progression 5. Conclusion
of pulmonary fibrosis. They can also release matrix In this study, we conducted an integrated analysis of gene
34
metalloproteinases to degrade the ECM, thereby reducing expression data to identify DEGs and key pathways in
its deposition. Evidence indicates that the M2 macrophage IPF. We discovered 215 DEGs, such as TMEM100, CPB2,
35
phenotype dominates during IPF progression, highlighting VIPR1, SPP1, and MMP7, with significant expression
36
the crucial role of macrophages in IPF development. changes in IPF. Functional analyses implicated these genes
According to a previous study, the number of CD8 T cells in ECM organization, ossification, and cell adhesion.
in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of patients with IPF was COL15A1 and COL6A3 were identified as hub genes with
correlated with the extent of lung fibrosis. Another study upregulated expression in IPF, suggesting their potential as
37
revealed that activated CD8 T cells are associated with therapeutic targets. Immune cell infiltration patterns in IPF
BLM-induced lung fibrosis. B cells and plasma cells are were also explored, revealing altered immune responses.
38
39
40
closely associated with the development and progression of Drug prediction and molecular docking identified (+)-
lung fibrosis. In addition, Treg cells, Th22 cells, Th17 cells, JQ1, aristolochic acid I, and dexamethasone as candidates
eosinophils, and other cell types have been implicated for IPF treatment. This study significantly advances our
in IPF, providing a theoretical basis for elucidating the understanding of IPF pathogenesis and provides valuable
36
mechanisms of IPF and the role of immune cell infiltration. insights for future therapeutic development.
This study predicted drugs targeting hub genes using
multiple databases, identifying compounds that affect Acknowledgments
the expression of hub genes, such as (+)-JQ1, aristolochic The authors extend their acknowledgments to all the
acid I, and dexamethasone. Molecular docking between participants of the study for their valuable contributions
COL15A1 and COL6A3 with their corresponding drugs to this project.
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 11 doi: 10.36922/gpd.4101