Page 87 - GPD-3-4
P. 87
Gene & Protein in Disease A prediction on how Epimedii herba treat periodontitis
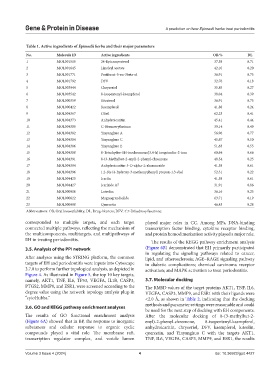
Table 1. Active ingredients of Epimedii herba and their major parameters
No. Molecule ID Active ingredients OB/% DL
1 MOL001510 24-Epicampesterol 37.58 0.71
2 MOL001645 Linoleyl acetate 42.10 0.20
3 MOL001771 Poriferast-5-en-3beta-ol 36.91 0.75
4 MOL001792 DFV 32.76 0.18
5 MOL003044 Chryseriol 35.85 0.27
6 MOL003542 8-Isopentenyl-kaempferol 38.04 0.39
7 MOL000359 Sitosterol 36.91 0.75
8 MOL000422 Kaempferol 41.88 0.24
9 MOL004367 Olivil 62.23 0.41
10 MOL004373 Anhydroicaritin 45.41 0.44
11 MOL004380 C-Homoerythrinan 39.14 0.49
12 MOL004382 Yinyanghuo A 56.96 0.77
13 MOL004384 Yinyanghuo C 45.67 0.50
14 MOL004386 Yinyanghuo E 51.63 0.55
15 MOL004388 8-Tetrahydro-1H-isochromeno[3,4-h] isoquinolin-2-ium 60.64 0.66
16 MOL004391 8-(3-Methylbut-2-enyl)-2-phenyl-chromone 48.54 0.25
17 MOL004394 Anhydroicaritin-3-O-alpha-L-rhamnoside 41.58 0.61
18 MOL004396 1,2-Bis (4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl) propan-1,3-diol 52.31 0.22
19 MOL004425 Icariin 41.58 0.61
20 MOL004427 Icariside A7 31.91 0.86
21 MOL000006 Luteolin 36.16 0.25
22 MOL000622 Magnograndiolide 63.71 0.19
23 MOL000098 Quercetin 46.43 0.28
Abbreviations: OB, Oral bioavailability; DL, Drug-likeness; DFV: 4',7-Dihydroxyflavanone.
corresponded to multiple targets, and each target played major roles in CC. Among MFs, DNA-binding
connected multiple pathways, reflecting the mechanism of transcription factor binding, cytokine receptor binding,
the multicomponents, multitargets, and multipathways of and protein homodimerization activity played a major role.
EH in treating periodontitis.
The results of the KEGG pathway enrichment analysis
3.5. Analysis of the PPI network (Figure 6B) demonstrated that EH primarily participated
in regulating the signaling pathways related to cancer,
After analyses using the STRING platform, the common lipid, and atherosclerosis; AGE–RAGE signaling pathway
targets of EH and periodontitis were inputs into Cytoscape in diabetic complications; chemical carcinoma receptor
3.7.0 to perform further topological analysis, as depicted in activation; and MAPK activation to treat periodontitis.
Figure 4. As illustrated in Figure 5, the top 10 key targets,
namely, AKT1, TNF, IL6, TP53, VEGFA, IL1B, CASP3, 3.7. Molecular docking
PTGS2, MMP9, and ESR1, were screened according to the The RMSD values of the target proteins AKT1, TNF, IL6,
degree value using the network topology analysis plug-in VEGFA, CASP3, MMP9, and ESR1 with their ligands were
“cytoHubba.” <2.0 Å, as shown in Table 2, indicating that the docking
3.6. GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses methods and parameter settings were reasonable and could
be used for the next step of docking with EH components.
The results of GO functional enrichment analysis After the molecular docking of 8-(3-methylbut-2-
(Figure 6A) showed that in BP, the response to inorganic enyl)-2-phenyl-chromone, 8-isopentenyl-kaempferol,
substances and cellular response to organic cyclic anhydroicaritin, chryseriol, DFV, kaempferol, luteolin,
compounds played a vital role. The membrane raft, quercetin, and Yinyanghuo C with the targets AKT1,
transcription regulator complex, and vesicle lumen TNF, IL6, VEGFA, CASP3, MMP9, and ESR1, the results
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 4 doi: 10.36922/gpd.4427