Page 92 - GPD-3-4
P. 92
Gene & Protein in Disease A prediction on how Epimedii herba treat periodontitis
A B
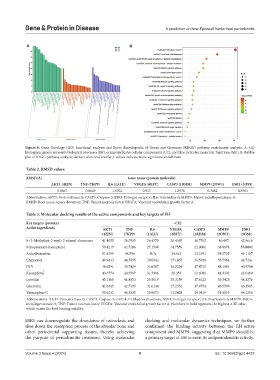
Figure 6. Gene Ontology (GO) functional analysis and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis. A: GO
histogram, green represents biological processes (BP), orange indicates cellular components (CC), and blue indicates molecular functions (MF). B: Bubble
plot of KEGG pathway analysis; darker colors and smaller p-values indicate more significant enrichment
Table 2. RMSD values
RMSD(Å) Gene name (protein molecule)
AKT1 (4EJN) TNF (7KP9) IL6 (1ALU) VEGFA (6BFT) CASP3 (1RHM) MMP9 (2OW1) ESR1 (3OS8)
0.8867 0.8649 1.6702 0.915 1.8978 0.3482 0.3963
Abbreviation: AKT1: Protein kinase B; CASP3: Caspase-3; ESR1: Estrogen receptor; IL6: Interleukin-6; MMP9: Matrix metalloproteinase-9;
RMSD: Root mean square deviation; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor VEGFA: Vascular endothelial growth factor A.
Table 3. Molecular docking results of the active components and key targets of EH
Key targets (protein) −CIE
Active ingredients AKT1 TNF IL6 VEGFA CASP3 MMP9 ESR1
(4EJN) (7KP9) (1ALU) (6BFT) (1RHM) (2OW1) (3OS8)
8-(3-Methylbut-2-enyl)-2-phenyl-chromone 41.4055 38.5565 26.4379 26.4365 16.7762 40.487 42.9618
8-Isopentenyl-kaempferol 50.4215 42.7286 27.1504 34.7559 22.0006 38.8674 55.0661
Anhydroicaritin 51.9299 44.596 N/A 34.412 22.2191 54.5735 49.1107
Chryseriol 40.9433 44.7695 30.0842 27.1465 20.5928 55.5964 44.7241
DFV 38.6591 38.7429 31.6587 26.2254 17.4715 48.1983 40.9704
Kaempferol 43.3774 40.5597 31.7986 26.355 22.6086 44.9292 43.0489
Luteolin 45.1168 41.8853 29.5019 29.3159 17.8122 53.5428 44.3276
Quercetin 42.6345 42.7105 31.6144 27.2352 17.6754 46.5599 46.3985
Yinyanghuo C 50.0232 46.3035 20.9673 32.2408 24.0419 51.8019 44.1256
Abbreviations: AKT1: Protein kinase B; CASP3: Caspase-3; DFV: 4',7-Dihydroxyflavanone; ESR1: Estrogen receptor; IL6: Interleukin-6; MMP9: Matrix
metalloproteinase-9; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor VEGFA: Vascular endothelial growth factor A. Numbers in bold represent the highest -CIE value,
which mains the best binding stability.
ESR1 can downregulate the abundance of osteoclasts and docking and molecular dynamics techniques, we further
slow down the resorption process of the alveolar bone and confirmed the binding activity between the EH-active
other periodontal supporting tissues, thereby achieving component and MMP9, suggesting that MMP9 should be
the purpose of periodontitis treatment. Using molecular a primary target of EH to exert its antiperiodontitis activity.
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 9 doi: 10.36922/gpd.4427