Page 94 - GPD-3-4
P. 94
Gene & Protein in Disease A prediction on how Epimedii herba treat periodontitis
A B C
D
E
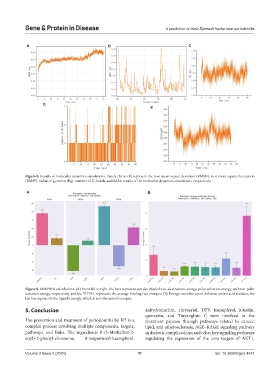
Figure 8. Results of molecular dynamics simulations. Panels (A) to (E) represent the root mean square deviation (RMSD), root mean square fluctuation
(RMSF), radius of gyration (Rg), number of H-bonds, and SASA results of the molecular dynamics simulations, respectively
A B
Figure 9. MMPBSA calculations. (A) From left to right, the bars represent van der Waals force, electrostatic energy, polar solvation energy, and non-polar
solvation energy, respectively, and the TOTAL represents the average binding free energies. (B) Energy contribution of different amino acid residues; the
last bar represents the ligand’s energy, which is also the sum of energies
5. Conclusion anhydroicaritin, chryseriol, DFV, kaempferol, luteolin,
quercetin, and Yinyanghuo C were involved in the
The prevention and treatment of periodontitis by EH is a treatment process through pathways related to cancer,
complex process involving multiple components, targets, lipid, and atherosclerosis; AGE–RAGE signaling pathway
pathways, and links. The ingredients 8-(3-Methylbut-2- in diabetic complications; and other key signaling pathways
enyl)-2-phenyl-chromone, 8-isopentenyl-kaempferol, regulating the expression of the core targets of AKT1,
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 11 doi: 10.36922/gpd.4427