Page 142 - GPD-4-1
P. 142
Gene & Protein in Disease Rotavirus diversity in Uttar Pradesh
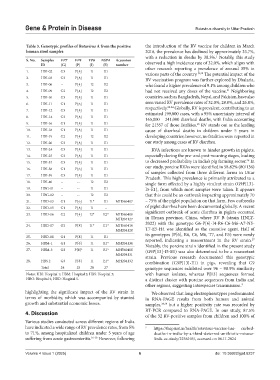
Table 3. Genotypic profiles of Rotavirus A from the positive the introduction of the RV vaccine for children in March
human stool samples 2016, the prevalence has declined by approximately 33.7%,
with a reduction in deaths by 38.3%. Notably, this study
1
S. No. Samples VP7 VP4 VP6 NSP4 Accession
ID (G) (P) (I) (E) number observed a high incidence rate of 32.0%, which aligns with
1. HBI-02 G3 P[8] I1 E1 other research reporting a prevalence of around 35% in
The potential impact of the
various parts of the country.
19,20
2. HBI-03 G3 P[8] I1 E1 RV vaccination program was further explored by Dhalaria,
3. HBI-06 -- P[4] I2 E2 who found a higher prevalence of 9.1% among children who
4. HBI-09 G2 P[4] I2 E2 had not received any doses of the vaccine. Neighboring
21
5. HBI-10 G3 P[8] I1 E1 countries, such as Bangladesh, Nepal, and Pakistan, have also
6. HBI-11 G1 P[6] I1 E1 seen varied RV prevalence rates of 32.0%, 28.0%, and 26.8%,
22-24
7. HBI-12 G3 P[8] I1 E1 respectively. Globally, RV is prevalent, contributing to an
estimated 199,000 cases, with a 95% uncertainty interval of
8. HBI-14 G3 P[8] I1 E1 165,000 – 241,000 diarrheal deaths, with India accounting
9. HBI-16 G1 P[8] I1 E1 for 21357 of those fatalities. RV stands out as the leading
25
10. HBI-18 G1 P[8] I1 E1 cause of diarrheal deaths in children under 5 years in
11. HBI-19 G2 P[4] I2 E2 developing countries; however, no fatalities were reported in
12. HBI-20 G3 P[8] I1 E1 our study among cases of RV diarrhea.
13. HBI-24 G3 P[8] I1 E1 RVA infections are known to hinder growth in piglets,
14. HBI-25 G3 P[8] I1 E1 especially during the pre- and post-weaning stages, leading
26
15. HBI-37 G3 P[8] I1 E1 to decreased profitability in India’s pig farming sector. In
16. HBI-38 G1 P[6] I1 E1 our study, porcine RVAs were identified in 58.82% (80/136)
17. HBI-39 G3 P[8] I1 E1 of samples collected from three different farms in Uttar
Pradesh. This high prevalence is primarily attributed to a
18. HBI-40 -- -- I2 E2 single farm affected by a highly virulent strain (G9P[13]-
19. HBG-01 -- -- I1 E1 I5-E1), from which most samples were taken. It appears
20. HBG-02 -- -- I2 E2 that this could be an outbreak impacting approximately 70
21. HBD-03 G1 P[6] I1* E1 MH560407 – 75% of the piglet population on that farm. Few outbreaks
22. HBD-05 G1 P[8] I1 -- of piglet diarrhea have been documented globally. A recent
23. HBD-06 G2 P[4] I2* E2* MH560409 significant outbreak of acute diarrhea in piglets occurred
MH204127 in Henan province, China, where RV B (strain HNLY-
24. HBD-07 G3 P[8] I1* E1* MH560410 2022) with the genotype G6-P[6]-I4-R6-C6-M6-A7-N5-
MH204128 T7-E5-H4 was identified as the causative agent. Half of
25. HBD-08 G1 P[8] I1 E1 its genotypes (P[6], R6, C6, M6, T7, and E5) were newly
reported, indicating a reassortment in the RV strain.
27
26. HBM-1 G1 P[6] I1 E1* MH204130 Notably, the porcine strain identified in the present study
27. HBM-3 G3 P[8]* I1 E1* MH560408 (G9P[13]-I5-E1) was also determined to be a reassortant
MH204131 strain. Previous research documented this genotypic
28. HBS 2 G3 P[8] I1 E1* MH204132 combination (G9P[13]-E1) in pigs, revealing that G9
Total 24 25 28 27 genotype sequences exhibited over 96 – 98.9% similarity
Notes: HBI: Hospital 1; HBM: Hospital 2; HBS: Hospital 3; with human isolates, whereas P[13] sequences formed
HBG: Hospital 4; HBD: Hospital 5. a distinct cluster with porcine sequences from India and
other regions, suggesting interspecies transmission. 9
highlighting the significant impact of the RV strain in We observed that long electropherotypes predominated
terms of morbidity, which was accompanied by stunted in RNA-PAGE results from both human and animal
growth and substantial economic losses. samples, 28,29 but a higher positivity rate was recorded by
4. Discussion RT-PCR compared to RNA-PAGE. In our study, 87.5%
of the 32 RV-positive samples from children and 100% of
Various studies conducted across different regions of India
have indicated a wide range of RV prevalence rates, from 5% 1 https://theprint.in/health/rotavirus-vaccine-has- curbed-
to 71%, among hospitalized children under 5 years of age deaths-in-india-by-a-third-deterred-antibiotic-misuse-
suffering from acute gastroenteritis. 16-18 However, following finds-us-study/2236105/, accessed on 06.11.2024
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 6 doi: 10.36922/gpd.6237