Page 15 - GPD-4-1
P. 15
Gene & Protein in Disease Gene fusions and chimeric RNAs
A B
C D
E F
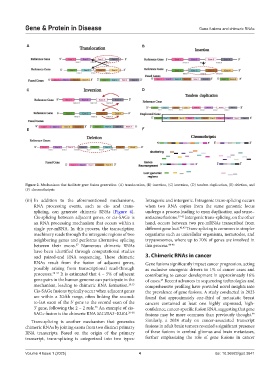
Figure 2. Mechanisms that facilitate gene fusion generation: (A) translocation, (B) insertion, (C) inversion, (D) tandem duplication, (E) deletion, and
(F) chromothripsis
(iii) In addition to the aforementioned mechanisms, Intragenic and intergenic. Intragenic trans-splicing occurs
RNA processing events, such as cis- and trans- when two RNA copies from the same genomic locus
splicing, can generate chimeric RNAs (Figure 4). undergo a process leading to exon duplication and sense–
Cis-splicing between adjacent genes, or cis-SAGe is antisense fusions. 39-41 Intergenic trans-splicing, on the other
an RNA processing mechanism that occurs within a hand, occurs between two pre-mRNAs transcribed from
single pre-mRNA. In this process, the transcription different gene loci. 42,43 Trans-splicing is common in simpler
machinery reads through the intergenic regions of two organisms such as unicellular organisms, nematodes, and
neighboring genes and performs alternative splicing trypanosomes, where up to 70% of genes are involved in
between their exons. Numerous chimeric RNAs this process. 44-46
27
have been identified through computational studies
and paired-end RNA sequencing. These chimeric 3. Chimeric RNAs in cancer
RNAs result from the fusion of adjacent genes, Gene fusions significantly impact cancer progression, acting
possibly arising from transcriptional read-through as exclusive oncogenic drivers in 1% of cancer cases and
processes. 28-34 It is estimated that 4 – 5% of adjacent contributing to cancer development in approximately 16%
gene pairs in the human genome can participate in the of cases. Recent advances in sequencing technologies and
47
mechanism, leading to chimeric RNA formation. 29,35 comprehensive profiling have provided novel insights into
Cis-SAGe fusions typically occur when adjacent genes the prevalence of gene fusions. A study conducted in 2023
are within a 30-kb range, often linking the second- found that approximately one-third of metastatic breast
to-last exon of the 5' gene to the second exon of the cancers contained at least one highly expressed, high-
3' gene, following the 2 – 2 rule. An example of cis- confidence, cancer-specific fusion RNA, suggesting that gene
36
SAGe fusion is the chimeric RNA SLC45A3–ELK4. 36-38 fusions may be more common than previously thought.
49
Trans-splicing is another mechanism that generates Similarly, a 2024 study on cancer-associated transcript
chimeric RNAs by joining exons from two distinct primary fusions in adult brain tumors revealed a significant presence
RNA transcripts. Based on the origin of the primary of these fusions in cerebral gliomas and brain metastases,
transcript, trans-splicing is categorized into two types: further emphasizing the role of gene fusions in cancer
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 4 doi: 10.36922/gpd.3641