Page 17 - GPD-4-1
P. 17
Gene & Protein in Disease Gene fusions and chimeric RNAs
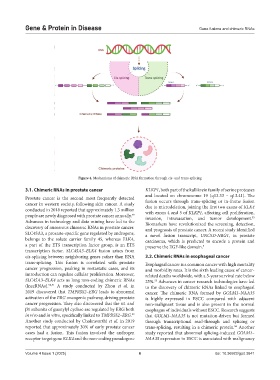
Figure 4. Mechanisms of chimeric RNA formation through cis- and trans-splicing
3.1. Chimeric RNAs in prostate cancer KLKP1, both part of the kallikrein family of serine proteases
Prostate cancer is the second most frequently detected and located on chromosome 19 (q13.33 – q13.41). The
cancer in western society, following skin cancer. A study fusion occurs through trans-splicing or in-frame fusion
due to microdeletion, joining the first two exons of KLK4
conducted in 2018 reported that approximately 1.3 million with exons 4 and 5 of KLKP1, affecting cell proliferation,
people are newly diagnosed with prostate cancer annually. invasion, intravasation, and tumor development.
49
53
Advances in technology and data mining have led to the Biomarkers have revolutionized the screening, detection,
discovery of numerous chimeric RNAs in prostate cancer. and prognosis of prostate cancer. A recent study identified
SLC45A3, a prostate-specific gene regulated by androgens, a novel fusion transcript, UNC5D-NRG1, in prostate
belongs to the solute carrier family 45, whereas ELK4, carcinoma, which is predicted to encode a protein and
a part of the ETS transcription factor group, is an ETS preserve the EGF-like domain. 9
transcription factor. SLC45A3–ELK4 fusion arises from
cis-splicing between neighboring genes rather than RNA 3.2. Chimeric RNAs in esophageal cancer
trans-splicing. This fusion is correlated with prostate Esophageal cancer is a common cancer with high mortality
cancer progression, peaking in metastatic cases, and its and morbidity rates. It is the sixth leading cause of cancer-
introduction can regulate cellular proliferation. Moreover, related deaths worldwide, with a 5-year survival rate below
SLC45A3–ELK4 acts as long non-coding chimeric RNAs 25%. Advances in cancer research technologies have led
55
(lnccRNAs). 50,51 A study conducted by Zhou et al. in to the discovery of chimeric RNAs linked to esophageal
2019 discovered that TMPRSS2–ERG leads to abnormal cancer. The chimeric RNA formed by GOLM1–NAA35
activation of the ERG oncogenic pathway, driving prostate is highly expressed in ESCC compared with adjacent
cancer progression. They also discovered that the α1 and non-malignant tissue and is also present in the normal
β1 subunits of guanylyl cyclase are regulated by ERG both esophagus of individuals without ESCC. Research suggests
in vivo and in vitro, specifically linked to TMPRSS2–ERG. that GOLMI–NAA35 is not mutation-driven but formed
52
Another study conducted by Chakravarthi et al. in 2019 through transcriptional read-through and splicing or
reported that approximately 30% of early prostate cancer trans-splicing, resulting in a chimeric protein. Another
56
cases had a fusion. This fusion involved the androgen study reported that abnormal splicing-induced GOLM1–
receptor target gene KLK4 and the non-coding pseudogene NAA35 expression in ESCC is associated with malignancy
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 6 doi: 10.36922/gpd.3641