Page 22 - GPD-4-1
P. 22
Gene & Protein in Disease Gene fusions and chimeric RNAs
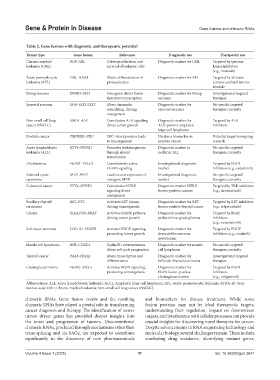
Table 2. Gene fusions with diagnostic and therapeutic potential
Tumor type Gene fusion Relevance Diagnostic use Therapeutic use
Chronic myeloid BCR–ABL Drives proliferation and Diagnostic marker for CML Targeted by tyrosine
leukemia (CML) survival of leukemic cells kinase inhibitors
(e.g., imatinib)
Acute promyelocytic PML–RARA Blocks differentiation of Diagnostic marker for APL Targeted by all-trans
leukemia (APL) promyelocytes retinoic acid and arsenic
trioxide
Ewing sarcoma EWSR1–FLI1 Oncogenic driver fusion Diagnostic marker for Ewing Investigational targeted
that alters transcription sarcoma therapies
Synovial sarcoma SS18–SSX1/SSX2 Alters chromatin Diagnostic marker for No specific targeted
remodeling, driving synovial sarcoma therapies currently
oncogenesis
Non-small cell lung EML4–ALK Constitutive ALK signaling Diagnostic marker for Targeted by ALK
cancer (NSCLC) drives tumor growth ALK-positive anaplastic inhibitors
large-cell lymphoma
Prostate cancer TMPRSS2–ERG ERG overexpression leads Used as a biomarker in Potential target in ongoing
to tumorigenesis prostate cancer research
Acute lymphoblastic ETV6–RUNX1 Promotes leukemogenesis Diagnostic marker in No specific targeted
leukemia (ALL) through altered pediatric ALL therapies currently
transcription
Glioblastoma FGFR3–TACC3 Constitutively active Investigational diagnostic Targeted by FGFR
FGFR3 signaling marker inhibitors (e.g., erdafitinib)
Adenoid cystic MYB–NFIB Leads to overexpression of Investigational diagnostic No specific targeted
carcinoma oncogene MYB marker therapies currently
Colorectal cancer ETV6–NTRK3 Constitutive NTRK Diagnostic marker NTRK Targeted by TRK inhibitors
signaling drives fusion-positive cancers (e.g., larotrectinib)
oncogenesis
Papillary thyroid RET–PTC Activates RET kinase, Diagnostic marker for RET Targeted by RET inhibitors
carcinoma driving tumorigenesis fusion-positive thyroid cancer (e.g., selpercatinib)
Glioma KIAA1549–BRAF Activates MAPK pathway, Diagnostic marker for Targeted by BRAF
driving tumor growth pediatric low-grade gliomas inhibitors
(e.g., vemurafenib)
Soft tissue sarcomas COL1A1–PDGFB Activates PDGF signaling, Diagnostic marker for Targeted by PDGF
promoting tumor growth dermatofibrosarcoma inhibitors (e.g., imatinib)
protuberans
Mantle cell lymphoma IGH–CCND1 Cyclin D1 overexpression Diagnostic marker for mantle No specific targeted
drives cell cycle progression cell lymphoma therapies currently
Thyroid cancer PAX8–PPARy Alters transcription and Diagnostic marker for Investigational targeted
differentiation follicular thyroid carcinoma therapies
Cholangiocarcinoma FGFR2–BICC1 Activates FGFR signaling, Diagnostic marker for Targeted by FGFR
promoting tumorigenesis FGFR fusion-positive inhibitors
cholangiocarcinoma (e.g., infigratinib)
Abbreviations: ALL: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia; ALCL: Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma; APL: Acute promyelocytic leukemia; ATRA: all-trans
retinoic acid; CML: Chronic myeloid leukemia; Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
chimeric RNAs. Gene fusion events and the resulting and biomarkers for disease treatment. While some
chimeric RNAs have played a pivotal role in transforming fusion proteins may not be ideal therapeutic targets,
cancer diagnosis and therapy. The identification of newer understanding their regulation, impact on downstream
tumor driver genes has provided deeper insights into targets, and interference with cellular processes can provide
the onset and progression of tumors. Unconventional crucial insights for discovering novel therapies for cancer.
chimeric RNAs, produced through mechanisms other than Despite advancements in RNA sequencing technology and
trans-splicing and cis-SAGe, are expected to contribute molecular biology, several challenges remain. These include
significantly to the discovery of new pharmaceuticals combating drug resistance, identifying mutant genes,
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 11 doi: 10.36922/gpd.3641