Page 82 - GTM-1-2
P. 82
Global Translational Medicine Succinate metabolism in CVD
and prevent obesity as well as metabolic dysfunction
caused by HFD in newborn mice . It is associated with
[73]
enhanced succinylation and H3K4me3 modification in the
PPARGC1A promoter. These results suggest that succinate
can promote energy consumption and counter obesity by
activating thermogenic fat, and this effect can be passed on
to offspring.
Succinate can increase the differentiation of beige
adipocytes. Stearoyl COA desaturase 1 (SCD1) is a rate-
limiting enzyme of monounsaturated fatty acids. SCD1
induces the differentiation of preadipocytes into beige
adipocytes through mitochondrial complex II activity
that is driven by succinate . Succinate inhibits the
[74]
decomposition of triglycerides in white fat through
SUCNR1 . The mitochondrial dicarboxylate vector
[75]
SLC25A10 is mainly expressed in white adipose tissue
(WAT), which enhances mitochondrial respiration,
promotes succinate transport to the outside of cells, and
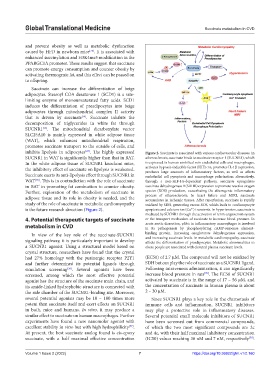
inhibits lipolysis in adipocytes . The highly expressed Figure 2. Succinate is associated with various cardiovascular diseases. In
[27]
SUCNR1 in WAT is significantly higher than that in BAT. atherosclerosis, succinate binds to succinate receptor 1 (SUCNR1), which
In the white adipose tissue of SUCNR1 knockout mice, is expressed in human umbilical vein endothelial cells and macrophages,
the inhibitory effect of succinate on lipolysis is weakened. activates hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α, promotes IL-1β expression,
produces large amounts of inflammatory factors, as well as affects
Succinate exerts its anti-lipolysis effect through SUCNR1 in endothelial cell pyroptosis and macrophage polarization; alternatively,
WAT . This is in contradiction with the role of succinate through a non-HIF-1α-dependent pathway, succinate upregulates
[76]
in BAT in promoting fat combustion to counter obesity. succinate dehydrogenase B (SDHB) expression to promote reactive oxygen
Further, exploration of the metabolism of succinate in species (ROS) production, exacerbating the atherogenic inflammatory
adipose tissue and its role in obesity is needed, and the process of atherosclerosis. In heart failure and MIRI, succinate
accumulates in ischemic tissues. After reperfusion, succinate is rapidly
study of the role of succinate in metabolic cardiomyopathy oxidized by SDH, generating excess ROS, which leads to cardiomyocyte
is the future research direction (Figure 2). apoptosis and calcium ion (Ca ) transients. In hypertension, succinate is
2+
mediated by SUCNR1 through the activation of renin-angiotensin system
4. Potential therapeutic targets of succinate or the transport mechanism of succinate to increase blood pressure. In
metabolism in CVD acute aortic dissection, p38α in inflammatory macrophages is involved
in its pathogenesis by phosphorylating cAMP-response element-
In view of the key role of the succinate-SUCNR1 binding protein, increasing oxoglutarate dehydrogenase expression,
signaling pathway, it is particularly important to develop and increasing succinate levels. In metabolic cardiomyopathy, succinate
affects the differentiation of preadipocytes. Metabolic abnormalities in
a SUCNR1 agonist. Using a structural model based on obese people are associated with elevated plasma succinate levels.
crystal structure, researchers have found that the crystal
had 27% homology with the purinergic receptor P2Y1 (EC50) of 2.7 μM. The compound will not be oxidized by
and further determined its potential ligands through SDH but can play the role of succinate as a SUCNR1 ligand.
simulation screening . Several agonists have been Following intravenous administration, it can significantly
[36]
[78]
screened, among which the most effective potential increase blood pressure in rats . The EC50 of SUCNR1
agonist has the structure of the succinate main chain, and activated by succinate is in the range of 17 – 56 μM, and
its amide-linked hydrophobic structure is connected with the concentration of succinate in human plasma is about
the side chamber of the SUCNR1-binding site. Moreover, 2 – 30 μM.
several potential agonists may be 10 – 100 times more Since SUCNR1 plays a key role in the chemotaxis of
potent than succinate itself and exert effects on SUCNR1 immune cells and inflammation, SUCNR1 inhibitors
in both, mice and humans. In vitro, it may produce a may play a protective role in inflammatory diseases.
similar effect to succinate on human macrophages. Further Several potential small molecule inhibitors of SUCNR1
experiments have found a new nanomolar agonist with have been screened out from commercial compounds,
excellent stability in vitro but with high hydrophilicity . of which the two most significant compounds are 2c
[77]
At present, the best succinate analog found is cis-epoxy and 4c, with their half maximal inhibitory concentration
succinate, with a half maximal effective concentration (IC50) values reaching 30 nM and 7 nM, respectively .
[79]
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2022) 7 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.v1i2.160