Page 16 - GTM-2-4
P. 16
Global Translational Medicine Keto diet in management of Type 2 diabetes
hepatocellular system, serving as an alternate fuel source transferred from white adipose tissue to hepatic cells, and
for most organs. The systemic contribution of ketone transformed into acetyl coenzyme A (CoA) . Acetyl
[37]
bodies to fuel ranges from 2% to 6% during prolonged CoA aggregates in a moderate environment and is then
fasting, escalating to approximately 30 – 40% after 2 days metabolized to acetoacetyl CoA by the enzyme thiolase.
of fasting . The three key ketone bodies synthesized Hydroxy-methylglutaryl (HMG) CoA oxidase catalyzes the
[36]
from hepatocytes are acetoacetate, acetone, and biosynthesis of 3-hydroxy-methylglutaryl CoA, leading to the
3-β-hydroxybutyrate. The latter is theoretically classified conversion of HMG CoA to acetoacetyl CoA and acetoacetate.
as a β-hydroxy acid rather than a true ketone body. Among Acetoacetate can be hydrolyzed to 3-hydroxybutyrate
these, 3-β-hydroxybutyrate appears to be the predominant through 3-β-hydroxybutyrate hydrogenase or converted to
ketone body molecule in plasma, followed by acetoacetate. acetone without enzyme involvement. Unused acetone, no
Notably, volatile acetone is predominantly lost through longer in use, is nevertheless primarily excreted through
respiration and is typically undetectable in the blood. urination and released through respiration.
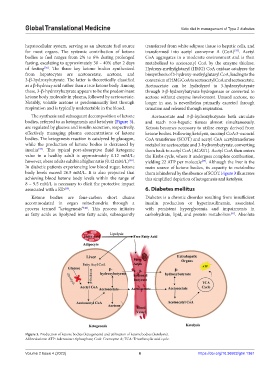
The synthesis and subsequent decomposition of ketone Acetoacetate and 3-β-hydroxybutyrate both circulate
bodies, referred to as ketogenesis and ketolysis (Figure 3), and reach non-hepatic tissues almost simultaneously.
are regulated by glucose and insulin secretion, respectively, Ketosis becomes necessary to utilize energy derived from
effectively managing plasma concentrations of ketone ketone bodies. Following ketolysis, succinyl CoA:3-oxoacid
bodies. The ketogenesis reaction is catalyzed by glucagon, CoA transferase (SCOT) and acetyl CoA acetyltransferase
while the production of ketone bodies is decreased by metabolize acetoacetate and 3-hydroxybutyrate, converting
insulin . This typical post-absorptive fluid ketogenic them back to acetyl CoA (ACAT1). Acetyl CoA then enters
[37]
value in a healthy adult is approximately 0.12 mM/L; the Krebs cycle, where it undergoes complete combustion,
however, obese adults exhibit a higher ratio (0.42 mM/L) . yielding 22 ATP per molecule . Although the liver is the
[38]
[37]
In diabetic patients experiencing low blood sugar, ketone main source of ketone bodies, its capacity to metabolize
body levels exceed 26.5 mM/L. It is also projected that them is hindered by the absence of SCOT. Figure 3 illustrates
achieving blood ketone body levels within the range of this simplified depiction of ketogenesis and ketolysis.
8 – 9.5 mM/L is necessary to elicit the protective impact
associated with a KD . 6. Diabetes mellitus
[39]
Ketone bodies are four-carbon short chains Diabetes is a chronic disorder resulting from insufficient
accommodated in organ mitochondria through a insulin production or hyperinsulinemia, associated
process termed “ketogenesis” . This process initiates with persistent hyperglycemia and impairments in
[40]
as fatty acids as lipolyzed into fatty acids, subsequently carbohydrate, lipid, and protein metabolism . Absolute
[41]
Figure 3. Production of ketone bodies (ketogenesis) and utilization of ketone bodies (ketolysis).
Abbreviations: ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; CoA: Coenzyme A; TCA: Tricarboxylic acid cycle.
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2023) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.1361