Page 13 - GTM-3-2
P. 13
Global Translational Medicine Mitochondria and ferroptotic cell death
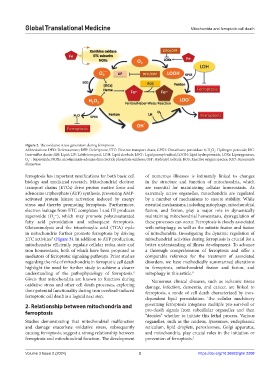
Figure 2. The oxidative stress generation during ferroptosis.
Abbreviations: DFO: Deferoxamine; DFP: Deferiprone; ETC: Electron transport chain; GPX4: Glutathione peroxidase 4; H O : Hydrogen peroxide; ISC:
2
2
Iron-sulfur cluster; LH: Lipid; LIP: Labile iron pool; LOH: Lipid alcohols; LOO : Lipid peroxyl radical; LOOH: Lipid hydroperoxide; LOXs: Lipoxygenases;
•
O : Superoxide; NOXs: nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidases; OH : Hydroxyl radicals; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; SOD: Superoxide
•–
•
2
dismutase.
ferroptosis has important ramifications for both basic cell of numerous illnesses is intimately linked to changes
biology and medicinal research. Mitochondrial electron in the structure and function of mitochondria, which
transport chains (ETCs) drive proton motive force and are essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis. As
adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthesis, preventing AMP- extremely active organelles, mitochondria are regulated
activated protein kinase activation induced by energy by a number of mechanisms to ensure stability. While
stress and thereby promoting ferroptosis. Furthermore, essential mechanisms, including mitophagy, mitochondrial
electron leakage from ETC complexes I and III produces fusion, and fission, play a major role in dynamically
superoxide (O ), which may promote polyunsaturated maintaining mitochondrial homeostasis, dysregulation of
•–
2
fatty acid peroxidation and subsequent ferroptosis. these processes can occur. Ferroptosis is closely associated
Glutaminolysis and the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle with mitophagy, as well as the mitotic fission and fusion
in mitochondria further promote ferroptosis by driving of mitochondria. Investigating the dynamic regulation of
ETC activities (Figure 3). In addition to ATP production, mitochondrial activities during ferroptosis is crucial for a
7
mitochondria efficiently regulate cellular redox state and better understanding of illness development. To advance
iron homeostasis, both of which have been proposed as a thorough comprehension of ferroptosis and offer a
mediators of ferroptotic signaling pathways. Prior studies comparable reference for the treatment of associated
regarding the role of mitochondria in ferroptotic cell death disorders, we have methodically summarized alterations
highlight the need for further study to achieve a clearer in ferroptosis, mitochondrial fission and fusion, and
understanding of the pathophysiology of ferroptosis. mitophagy in this article. 9
8
Given that mitochondria are known to function during Numerous clinical diseases, such as ischemic tissue
oxidative stress and other cell death processes, exploring damage, infection, dementia, and cancer, are linked to
their potential functionality during iron overload-induced ferroptosis, a mode of cell death characterized by iron-
ferroptotic cell death is a logical next step. dependent lipid peroxidation. The cellular machinery
2. Relationship between mitochondria and governing ferroptosis integrates multiple pro-survival or
ferroptosis pro-death signals from subcellular organelles and then
“decides” whether to initiate this lethal process. Various
Studies demonstrating that mitochondrial malfunction organelles, such as the nucleus, lysosomes, endoplasmic
and damage exacerbate oxidative stress, subsequently reticulum, lipid droplets, peroxisomes, Golgi apparatus,
causing ferroptosis, suggest a strong relationship between and mitochondria, play crucial roles in the initiation or
ferroptosis and mitochondrial function. The development prevention of ferroptosis. 5
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.2208