Page 14 - GTM-3-2
P. 14
Global Translational Medicine Mitochondria and ferroptotic cell death
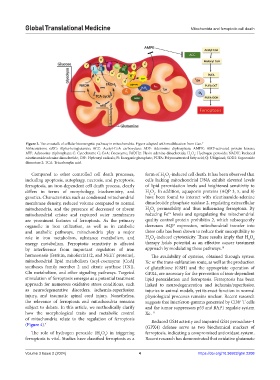
Figure 3. The crosstalk of cellular bioenergetic pathway in mitochondria. Figure adapted with modification from Gan. 7
Abbreviations: αKG: Alpha-ketoglutarate; ACC: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase; ADP: Adenosine diphosphate; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase;
ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; C: Cytochrome C; CoA: Coenzyme; FADH2: Flavin adenine dinucleotide; H O : Hydrogen peroxide; NADH: Reduced
2
2
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; OH : Hydroxyl radicals; Pi: Inorganic phosphate; PUFA: Polyunsaturated fatty acid; Q: Ubiquinol; SOD2: Superoxide
•
dismutase 2; TCA: Tricarboxylic acid.
Compared to other controlled cell death processes, form of H O -induced cell death. It has been observed that
2
2
including apoptosis, autophagy, necrosis, and pyroptosis, cells lacking mitochondrial DNA exhibit elevated levels
ferroptosis, an iron-dependent cell death process, clearly of lipid peroxidation levels and heightened sensitivity to
differs in terms of morphology, biochemistry, and H O . In addition, aquaporin proteins (AQP 3, 5, and 8)
2
2
genetics. Characteristics such as condensed mitochondrial have been found to interact with nicotinamide-adenine
membrane density, reduced volume compared to normal dinucleotide phosphate oxidase 2, regulating extracellular
mitochondria, and the presence of decreased or absent H O permeability and thus influencing ferroptosis. By
2
2
2+
mitochondrial cristae and ruptured outer membranes reducing Fe levels and upregulating the mitochondrial
are prominent features of ferroptosis. As the primary quality control protein prohibitin 2, which subsequently
organelle in iron utilization, as well as in catabolic decreases AQP expression, mitochondrial transfer into
and anabolic pathways, mitochondria play a major these cells has been shown to reduce their susceptibility to
role in iron metabolism, substance metabolism, and H O -induced cytotoxicity. These results imply that H O
2
2
2
2
energy metabolism. Ferroptotic sensitivity is affected therapy holds potential as an effective cancer treatment
by interference from important regulators of iron approach by modulating these pathways. 10
homeostasis (ferritin, mitoferrin1/2, and NEET proteins), The availability of cysteine, obtained through system
mitochondrial lipid metabolism (acyl-coenzyme [CoA] Xc or the trans-sulfuration route, as well as the production
-
syntheses family member 2 and citrate synthase [CS]), of glutathione (GSH) and the appropriate operation of
Gln metabolism, and other signaling pathways. Targeted GPX4, are necessary for the prevention of iron-dependent
stimulation of ferroptosis emerges as a potential treatment lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. Ferroptosis has been
approach for numerous oxidative stress conditions, such linked to neurodegeneration and ischemia/reperfusion
as neurodegenerative disorders, ischemia-reperfusion injuries in animal models, yet its exact function in normal
injury, and traumatic spinal cord injury. Nonetheless, physiological processes remains unclear. Recent research
the relevance of ferroptosis and mitochondria remains suggests that interferon-gamma generated by CD8 T cells
+
subject to debate. In this article, we methodically clarify and the tumor suppressors p53 and BAP1 regulate system
how the morphological traits and metabolic control Xc . - 11
of mitochondria relate to the regulation of ferroptosis Reduced GSH activity and impaired GSH peroxidase-4
(Figure 4). 4
(GPX4) defense serve as two biochemical markers of
The role of hydrogen peroxide (H O ) in triggering ferroptosis, indicating a compromised antioxidant system.
2
2
ferroptosis is vital. Studies have classified ferroptosis as a Recent research has demonstrated that oxidative glutamate
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.2208