Page 18 - GTM-3-2
P. 18
Global Translational Medicine Mitochondria and ferroptotic cell death
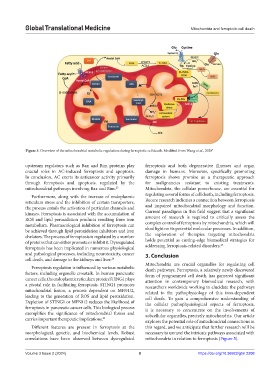
Figure 5. Overview of the mitochondrial metabolic regulation during ferroptotic cell death. Modified from Wang et al., 2020 4
upstream regulators such as Bax and Bim proteins play ferroptosis and both degenerative illnesses and organ
crucial roles in AC-induced ferroptosis and apoptosis. damage in humans. Moreover, specifically promoting
In conclusion, AC exerts its anticancer activity primarily ferroptosis shows promise as a therapeutic approach
through ferroptosis and apoptosis, regulated by the for malignancies resistant to existing treatments.
mitochondrial pathways involving Bax and Bim. 23 Mitochondria, the cellular powerhouse, are essential for
Furthermore, along with the increase of endoplasmic regulating several forms of cell death, including ferroptosis.
reticulum stress and the inhibition of certain transporters, Recent research indicates a connection between ferroptosis
the process entails the activation of particular channels and and impaired mitochondrial morphology and function.
kinases. Ferroptosis is associated with the accumulation of Current paradigms in this field suggest that a significant
ROS and lipid peroxidation products resulting from iron amount of research is required to critically assess the
metabolism. Pharmacological inhibition of ferroptosis can complex control of ferroptosis by mitochondria, which will
be achieved through lipid peroxidation inhibitors and iron shed light on its potential molecular processes. In addition,
chelators. The process of ferroptosis is regulated by a number the exploration of therapies targeting mitochondria
of proteins that can either promote or inhibit it. Dysregulated holds potential as cutting-edge biomedical strategies for
26
ferroptosis has been implicated in numerous physiological addressing ferroptosis-related disorders.
and pathological processes, including neurotoxicity, cancer 3. Conclusion
cell death, and damage to the kidneys and liver. 24
Mitochondria are crucial organelles for regulating cell
Ferroptosis regulation is influenced by various metabolic death pathways. Ferroptosis, a relatively newly discovered
factors, including organelle crosstalk. In human pancreatic form of programmed cell death, has garnered significant
cancer cells, the endoplasmic reticulum protein STING1 plays attention in contemporary biomedical research, with
a pivotal role in facilitating ferroptosis. STING1 promotes researchers worldwide working to elucidate the pathways
mitochondrial fusion, a process dependent on MFN1/2, related to the pathophysiology of this iron-dependent
leading to the generation of ROS and lipid peroxidation. cell death. To gain a comprehensive understanding of
Depletion of STING1 or MFN1/2 reduces the likelihood of the cellular pathophysiological aspects of ferroptosis,
ferroptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. This biological process it is necessary to concentrate on the involvements of
exemplifies the significance of mitochondrial fusion and subcellular organelles, precisely mitochondria. Our article
carries important therapeutic implications. 25 explores the potential role of mitochondrial connections in
Different features are present in ferroptosis at the this regard, and we anticipate that further research will be
morphological, genetic, and biochemical levels. Robust necessary to unravel the intricate pathways associated with
correlations have been observed between dysregulated mitochondria in relation to ferroptosis (Figure 5).
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 8 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.2208