Page 15 - GTM-3-2
P. 15
Global Translational Medicine Mitochondria and ferroptotic cell death
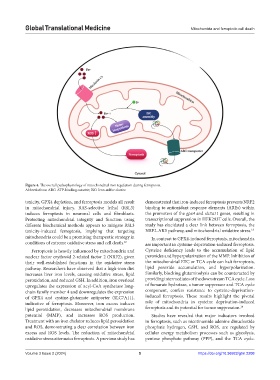
Figure 4. The overall pathophysiology of mitochondrial iron regulation during ferroptosis.
Abbreviations: ABC: ATP-binding cassette; ISC: Iron-sulfur cluster.
toxicity, GPX4 depletion, and ferroptosis models all result demonstrated that iron-induced ferroptosis prevents NRF2
in mitochondrial injury. RAS-selective lethal (RSL3) binding to antioxidant response elements (AREs) within
induces ferroptosis in neuronal cells and fibroblasts. the promoters of the gpx4 and slc7a11 genes, resulting in
Protecting mitochondrial integrity and function using transcriptional suppression in HEK293T cells. Overall, the
different biochemical methods appears to mitigate RSL3 study has elucidated a clear link between ferroptosis, the
toxicity-induced ferroptosis, implying that targeting NRF2-ARE pathway, and mitochondrial oxidative stress. 13
mitochondria could be a promising therapeutic strategy in In contrast to GPX4-induced ferroptosis, mitochondria
conditions of extreme oxidative stress and cell death. 12 are important in cysteine-deprivation-induced ferroptosis.
Ferroptosis is heavily influenced by mitochondria and Cysteine deficiency leads to the accumulation of lipid
nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2), given peroxides and hyperpolarization of the MMP. Inhibition of
their well-established functions in the oxidative stress the mitochondrial ETC or TCA cycle can halt ferroptosis,
pathway. Researchers have observed that a high-iron diet lipid peroxide accumulation, and hyperpolarization.
increases liver iron levels, causing oxidative stress, lipid Similarly, blocking glutaminolysis can be counteracted by
peroxidation, and reduced GSH. In addition, iron overload providing intermediates of the downstream TCA cycle. Loss
upregulates the expression of acyl-CoA synthetase long- of fumarate hydratase, a tumor suppressor and TCA cycle
chain family member 4 and downregulates the expression component, confers resistance to cysteine-deprivation-
of GPX4 and cystine-glutamate antiporter (SLC7A11), induced ferroptosis. These results highlight the pivotal
indicative of ferroptosis. Moreover, iron excess induces role of mitochondria in cysteine deprivation-induced
lipid peroxidation, decreases mitochondrial membrane ferroptosis and its potential for tumor suppression. 14
potential (MMP), and increases ROS production. Studies have revealed that major indicators involved
Treatment with an iron chelator reduces lipid peroxidation in ferroptosis, such as nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
and ROS, demonstrating a clear correlation between iron phosphate hydrogen, GSH, and ROS, are regulated by
excess and ROS levels. The reduction of mitochondrial cellular energy metabolism processes such as glycolysis,
oxidative stress attenuates ferroptosis. A previous study has pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), and the TCA cycle.
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.2208