Page 46 - GTM-3-2
P. 46
Global Translational Medicine Prognostic indicators and management of SAP
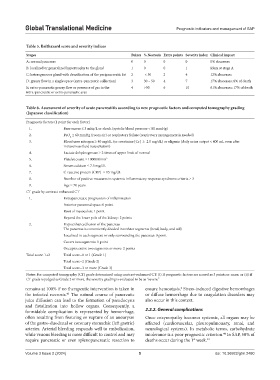
Table 5. Balthazard score and severity indices
Stages Points % Necrosis Extra points Severity index Clinical impact
A: normal pancreas 0 0 0 0 0% abscesses
B: localized or generalized hypertrophy to the gland 1 0 0 1 Idem at stage A
C: heterogeneous gland with densification of the peripancreatic fat 2 < 30 2 4 12% abscesses
D: greasy flow in a single space (extra‑pancreatic collection) 3 30 – 50 4 7 17% abscesses; 8% of death
E: extra-pancreatic greasy flow or presence of gas in the 4 >50 6 10 61% abscesses; 17% of death
intra-pancreatic or extra-pancreatic area
Table 6. Assessment of severity of acute pancreatitis according to new prognostic factors and computed tomography grading
(Japanese classification)
Prognostic factors (1 point for each factor)
1. Base excess ≤ 3 mEq/L or shock (systolic blood pressure < 80 mmHg)
2. PaO ≤ 60 mmHg (room air) or respiratory failure (respiratory management is needed)
2
3. Blood urea nitrogen ≥ 40 mg/dL (or creatinine [Cr] ≥ 2.0 mg/dL) or oliguria (daily urine output < 400 mL even after
intravenous fluid resuscitation)
4. Lactate dehydrogenase ≥ 2 times of upper limit of normal
5. Platelet count ≤ 100000/mm 3
6. Serum calcium ≤ 7.5 mg/dL
7. C-reactive protein (CRP) ≥ 15 mg/dL
8. Number of positive measures in systemic inflammatory response syndrome criteria ≥ 3
9. Age ≥ 70 years
CT grade by contrast-enhanced CT
1. Extrapancreatic progression of inflammation
Anterior pararenal space: 0 point
Root of mesocolon: 1 point
Beyond the lower pole of the kidney: 2 points
2. Hypoenhanced lesion of the pancreas
The pancreas is conveniently divided into three segments (head, body, and tail)
Localized in each segment or only surrounding the pancreas: 0 point
Covers two segments: 1 point
Occupies entire two segments or more: 2 points
Total score: 1+2 Total score=0 or 1 (Grade 1)
Total score=2 (Grade 2)
Total score=3 or more (Grade 3)
Notes: For computed tomography (CT) grade determined using contrast-enhanced CT: (i) If prognostic factors are scored as 3 points or more, or (ii) if
CT grade is judged as Grade 2 or more, the severity grading is evaluated to be as “severe.”
remains at 100% if no therapeutic intervention is taken in ensure hemostasis. Stress-induced digestive hemorrhages
2
the infected necrosis. The natural course of pancreatic or diffuse hemorrhage due to coagulation disorders may
43
juice diffusion can lead to the formation of pseudocysts also occur in this context.
and fistulization into hollow organs. Consequently, a
formidable complication is represented by hemorrhage, 2.2.2. General complications
often resulting from fissuring or rupture of an aneurysm Once enzymopathy becomes systemic, all organs may be
of the gastro-duodenal or coronary stomachic (left gastric) affected (cardiovascular, pleuropulmonary, renal, and
arteries. Arterial bleeding responds well to embolization, neurological systems). In metabolic terms, carbohydrate
while venous bleeding is more difficult to control and may intolerance is a poor prognostic criterion. In SAP, 50% of
44
require pancreatic or even splenopancreatic resection to deaths occur during the 1 week. 44
st
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 5 doi: 10.36922/gtm.2480