Page 15 - GTM-3-3
P. 15
Global Translational Medicine Influence of estrogen on RV mitochondria in PH
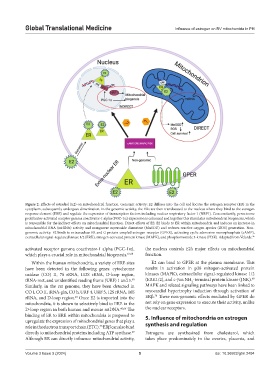
Figure 2. Effects of estradiol (E2) on mitochondrial function. Genomic activity: E2 diffuses into the cell and locates the estrogen receptor (ER) in the
cytoplasm, subsequently undergoes dimerization. In the genomic activity, the ERs are then translocated to the nucleus where they bind to the estrogen
response element (ERE) and regulate the expression of transcription factors including nuclear respiratory factor 1 (NRF1). Concomitantly, peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1 alpha (PGC-1α) expression is enhanced and together this stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis, which
is responsible for the indirect effects on mitochondrial function. Direct effects of E2: E2 binds to ER within mitochondria and induces an increase in
mitochondrial RNA (mtRNA) activity and manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) and reduces reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. Non-
genomic activity: E2 binds to extranuclear ER and G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER), activating cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP),
extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K). Adapted from Velarde. 36
activated receptor gamma coactivator-1 alpha (PGC-1α), the nucleus controls E2’s major effects on mitochondrial
which plays a crucial role in mitochondrial biogenesis. 67,68 function.
Within the human mitochondria, a variety of ERE sites E2 can bind to GPER at the plasma membrane. This
have been detected in the following genes: cytochrome results in activation in p38 mitogen-activated protein
oxidase (CO) II, 7S rRNA, 112S rRNA, D-loop region, kinases (MAPK), extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2
68
tRNA-met, and unidentified reading frame (URF) 1 and 5. (ERK1/2), and c-Jun NH -terminal protein kinase (JNK).
60
2
Similarly, in the rat genome, they have been detected in MAPK and related signaling pathways have been linked to
CO I, CO II, tRNA-gIn, CO b, URF 4, URF 5, 12S rRNA, 16S myocardial hypertrophy induction through activation of
70
rRNA, and D-loop region. Once E2 is imported into the ERβ. These non-genomic effects mediated by GPER do
60
mitochondria, it is shown to selectively bind to ERE in the not rely on gene expression to execute their activity, unlike
D-loop region in both human and mouse mtDNA. 60,66 The the nuclear receptors.
binding of ER to ERE within mitochondria is proposed to 5. Influence of mitochondria on estrogen
upregulate the expression of mitochondrial genes that play a
role in the electron transport chain (ETC). ERβ can also bind synthesis and regulation
36
directly to mitochondrial proteins including ATP synthase. Estrogens are synthesized from cholesterol, which
69
Although ER can directly influence mitochondrial activity, takes place predominately in the ovaries, placenta, and
Volume 3 Issue 3 (2024) 5 doi: 10.36922/gtm.2494