Page 52 - GTM-3-4
P. 52
Global Translational Medicine Eco-friendly biomedical materials: A review
many pathogens and green synthesis does increase the
biocompatibility of these materials, this activity can also
negatively impact human cells and tissues in the long
term as noted by Mao et al. who presented how the
31
production of reactive oxygen species, which are some of
the substances responsible for the antimicrobial effect of
AgNPs and can also cause apoptosis, DNA damage, and
autophagy in human cells. This also occurs with other
31
types of metallic nanoparticles, such as Cu/CuO, Au ,
33
32
and ZnO. 34
2.2. Copper and copper-based nanoparticles
(CuNPs)
CuNPs are common materials in biomedical applications
due to their antimicrobial properties and low toxicity.
35
These properties are derived from the metallic ions
formed during synthesis, which induce a decrease in the
transmembrane electrochemical potential of the bacteria,
which consequently causes an integrity loss of the cell
membrane leading to oxidative stress and cellular death
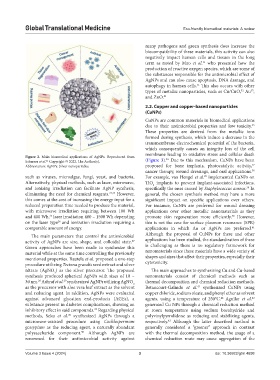
Figure 2. Main biomedical applications of AgNPs. Reproduced from 36
21
Sabarees et al. Copyright © 2022, The Author(s). (Figure 3). Due to this mechanism, CuNPs have been
37
Abbreviation: AgNPs: Silver nanoparticles. proposed for bone implants, photocatalytic activity,
cancer therapy, wound dressings, and oral applications.
38
such as viruses, microalgae, fungi, yeast, and bacteria. For example, van Hengel et al. implemented CuNPs on
39
Alternatively, physical methods, such as laser, microwave, TiO implants to prevent implant-associated infections,
2
and ionizing irradiation can facilitate AgNP synthesis, specifically the ones caused by Staphylococcus aureus. In
39
eliminating the need for chemical reagents. 23,24 However, general, the chosen synthesis method may have a more
this comes at the cost of increasing the energy input for a significant impact on specific applications over others.
reduced preparation time needed to produce the material, For instance, CuNPs are preferred for wound dressing
with microwave irradiation requiring between 100 Wh applications over other metallic nanomaterials as they
and 400 Wh, laser irradiation 400 – 1500 Wh depending promote skin regeneration more efficiently. However,
25
40
on the laser type and ionization irradiation requiring a this is not the case for surface plasmon resonance (SPR)
26
comparable amount of energy. applications in which Au or AgNPs are preferred.
41
The main parameters that control the antimicrobial Although the proposal of CuNPs for these and other
activity of AgNPs are size, shape, and colloidal state. applications has been studied, the standardization of these
27
Green approaches have been made to synthesize this is challenging as there is no regulatory framework for
material while at the same time controlling the previously nanomaterials since these materials have a wide variety of
mentioned properties. Rautela et al. proposed a one-step shapes and sizes that affect their properties, especially their
procedure utilizing Tectona grandis seed extract and silver cytotoxicity.
nitrate (AgNO ) as the silver precursor. The proposed The main approaches to synthesizing Cu and Cu-based
3
synthesis produced spherical AgNPs with sizes of 10 – nanomaterials consist of chemical methods such as
30 nm. Ashraf et al. synthesized AgNPs utilizing AgNO thermal decomposition and chemical reduction methods.
29
28
3
as the precursor with aloe vera leaf extract as the solvent Betancourt-Galindo et al. synthesized CuNPs using
42
and reducing agent. In addition, AgNPs were evaluated copper chloride, sodium oleate, and phenyl ether as solvent
against advanced glycation end-products (AGEs), a agents, using a temperature of 250°C. Aguilar et al.
42
43
substance present in diabetes complications, showing an generated Cu NPs through a chemical reduction method
inhibitory effect in said compounds. Regarding physical at room temperature using sodium borohydride and
29
30
methods, Seku et al. synthesized AgNPs through a polyvinylpyrrolidone as reducing and stabilizing agents,
microwave-assisted procedure using Cochlospermum respectively. Although the latter described method is
43
gossypium as the reducing agent, a naturally abundant generally considered a “greener” approach in contrast
polysaccharide component. Although AgNPs are with the thermal decomposition method, the usage of a
30
renowned for their antimicrobial activity against chemical reduction route may cause aggregation of the
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 3 doi: 10.36922/gtm.4698