Page 54 - GTM-3-4
P. 54
Global Translational Medicine Eco-friendly biomedical materials: A review
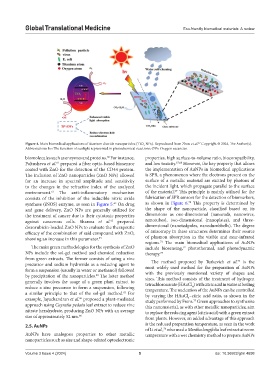
Figure 4. Main biomedical applications of titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO NPs). Reproduced from Zhou et al. Copyright © 2024, The Author(s).
47
2
Abbreviations: hv: The function of sunlight represented in photochemical reactions; OVs: Oxygen vacancies.
biomolecules such as enzymes and proteins. For instance, properties, high surface-to-volume ratio, biocompatibility,
60
Paltusheva et al. prepared a fiber optic-based biosensor and low toxicity. 67,68 However, the key property that allows
61
coated with ZnO for the detection of the CD44 protein. the implementation of AuNPs in biomedical applications
The inclusion of ZnO nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) allowed is SPR, a phenomenon where the electrons present on the
for an increase in spectral amplitude and sensitivity surface of a metallic material are excited by photons of
to the changes in the refractive index of the analyzed the incident light, which propagate parallel to the surface
69
61
environment. The anti-inflammatory mechanism of the material. This principle is mainly utilized for the
consists of the inhibition of the inducible nitric oxide fabrication of SPR sensors for the detection of biomarkers,
70
synthase (iNOS) enzyme, as seen in Figure 5. On drug as shown in Figure 6. This property is determined by
62
and gene delivery, ZnO NPs are generally utilized for the shape of the nanoparticle, classified based on its
the treatment of cancer due to their cytotoxic properties dimensions as one-dimensional (nanorods, nanowires,
against cancerous cells. Sharma et al. prepared nanotubes), two-dimensional (nanoplates), and three-
63
doxorubicin-loaded ZnO NPs to evaluate the therapeutic dimensional (nanotadpoles, nanodumbbells). The degree
efficacy of the combination of said compound with ZnO, of anisotropy in these structures determines their source
showing an increase in this parameter. 63 of plasmon absorption in the visible and near-infrared
regions. The main biomedical applications of AuNPs
71
The main green methodologies for the synthesis of ZnO include biosensing, photothermal, and photodynamic
72
NPs include the sol-gel method and chemical reduction therapy. 73
from green extracts. The former consists of using a zinc 74
precursor and sodium hydroxide as a reducing agent to The method proposed by Turkevich et al. is the
form a suspension (usually in water or methanol) followed most widely used method for the preparation of AuNPs
by precipitation of the nanoparticles. The latter method with the previously mentioned variety of shapes and
64
sizes. This method consists of the treatment of hydrogen
generally involves the usage of a green plant extract to tetrachloroaurate (HAuCl ) with citric acid in water at boiling
reduce a zinc precursor to form a suspension, following temperature. The nucleation of the AuNPs can be controlled
4
a similar principle to that of the sol-gel method. For by varying the HAuCl –citric acid ratio, as shown in the
65
4
example, Jayachandran et al. proposed a plant-mediated study performed by Frens. Green approaches to synthesize
66
75
approach using Cayratia pedata leaf extract to reduce zinc this nanomaterial, as with other metallic nanoparticles; aim
nitrate hexahydrate, producing ZnO NPs with an average to replace the reducing agent (citric acid) with a green extract
size of approximately 52 nm. 66 from plants. However, an added advantage of this approach
2.5. AuNPs is the reduced preparation temperature, as seen in the work
of Li et al., who used a Mentha longifolia leaf extract at room
76
AuNPs have analogous properties to other metallic temperature with a wet chemistry method to prepare AuNPs
nanoparticles such as size and shape-related optoelectronic
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 5 doi: 10.36922/gtm.4698