Page 85 - GTM-4-2
P. 85
Global Translational Medicine Angiotensinogen in liver steatosis
A
B C
D E
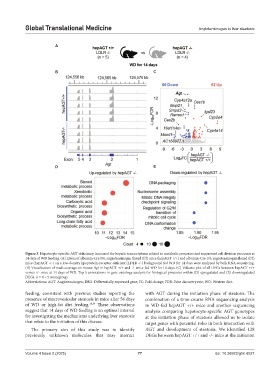
Figure 3. Hepatocyte-specific AGT deficiency increased the hepatic transcriptome related to metabolic processes and suppressed cell division processes at
14 days of WD feeding. (A) Livers of albumin-Cre 0/0; angiotensinogen floxed (f/f) mice (hepAGT +/+) and albumin-Cre 1/0; angiotensinogen floxed (f/f)
mice (hepAGT -/-) on a low-density lipoprotein-receptor deficient (LDLR -/-) background fed WD for 14 days were analyzed by bulk RNA sequencing.
(B) Visualization of read coverage on mouse Agt in hepAGT +/+ and -/- mice fed WD for 14 days. (C) Volcano plot of all DEGs between hepAGT +/+
versus -/- mice at 14 days of WD. Top 5 annotations in gene ontology analysis for biological processes within (D) upregulated and (E) downregulated
DEGs. n = 4 – 5 mice/group.
Abbreviations: AGT: Angiotensinogen; DEG: Differentially expressed gene; FC: Fold change; FDR: False discovery rate; WD: Western diet.
feeding, consistent with previous studies reporting the with AGT during the initiation phase of steatosis. The
presence of macrovesicular steatosis in mice after 56 days combination of a time-course RNA sequencing analysis
of WD or high-fat diet feeding. 28,34 These observations in WD-fed hepAGT +/+ mice and another sequencing
suggest that 14 days of WD feeding is an optimal interval analysis comparing hepatocyte-specific AGT genotypes
for investigating the mechanisms underlying liver steatosis at the initiation phase of steatosis allowed us to isolate
that relate to the initiation of this disease. target genes with potential roles in both interaction with
The primary aim of this study was to identify AGT and development of steatosis. We identified 128
previously unknown molecules that may interact DEGs between hepAGT +/+ and -/- mice at the initiation
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 77 doi: 10.36922/gtm.6027