Page 87 - GTM-4-2
P. 87
Global Translational Medicine Angiotensinogen in liver steatosis
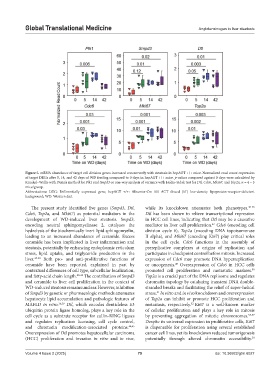
Figure 5. mRNA abundance of target cell division genes increased concurrently with steatosis in hepAGT +/+ mice. Normalized read count expression
of target DEGs after 5, 14, and 42 days of WD feeding compared to 0 days in hepAGT +/+ mice. p-values compared against 0 days were calculated by
Kruskal–Wallis with Dunn’s method for Plk1 and Smpd3 or one-way analysis of variance with Holm–Sidak test for Dtl, Cdc6, Mki67, and Top2a. n = 4 – 5
mice/group.
Abbreviations: DEG: Differentially expressed gene; hepAGT +/+: Albumin-Cre 0/0 AGT floxed (f/f) low-density lipoprotein-receptor-deficient
background; WD: Western diet.
The present study identified five genes (Smpd3, Dtl, while its knockdown attenuates both phenotypes. 46-48
Cdc6, Top2a, and Mki67) as potential mediators in the Dtl has been shown to relieve transcriptional repression
development of WD-induced liver steatosis. Smpd3, in HCC cell lines, indicating that Dtl may be a causative
encoding neutral sphingomyelinase 2, catalyzes the mediator in liver cell proliferation. Cdc6 (encoding cell
47
hydrolysis of the biochemically inert lipid sphingomyelin, division cycle 6), Top2a (encoding DNA topoisomerase
leading to an increased abundance of ceramide. Excess II alpha), and Mki67 (encoding Ki67) play critical roles
ceramide has been implicated in liver inflammation and in the cell cycle. Cdc6 functions in the assembly of
steatosis, potentially by enhancing endoplasmic reticulum prereplicative complexes at origins of replication and
stress, lipid uptake, and triglyceride production in the participates in checkpoint control before mitosis. Increased
liver. 35-39 Both pro- and anti-proliferative functions of expression of Cdc6 may promote DNA hyperreplication
ceramide have been reported, explained in part by or oncogenesis. Overexpression of Cdc6 in HCC cells
49
contextual differences of cell type, subcellular localization, promoted cell proliferation and metastatic markers.
50
and fatty-acid chain length. 40-43 The contribution of Smpd3 Top2a is a crucial part of the DNA replisome and regulates
and ceramide to liver cell proliferation in the context of chromatin topology by catalyzing transient DNA double-
WD-induced steatosis remains unclear. However, inhibition stranded breaks and facilitating the relief of super-helical
of Smpd3 by genetic or pharmacologic methods attenuates stress. In vitro and in vivo knockdown and overexpression
51
hepatocyte lipid accumulation and pathologic features of of Top2a can inhibit or promote HCC proliferation and
MAFLD in vitro. 36,39 Dtl, which encodes denticleless E3 metastasis, respectively. Ki67 is a well-known marker
52
ubiquitin protein ligase homolog, plays a key role in the of cellular proliferation and plays a key role in mitosis
cell cycle as a substrate receptor for cullin-RING ligases by preventing aggregation of mitotic chromosomes. 53-57
and regulates replication licensing, cell cycle control, Despite its universal expression in proliferative cells, Ki67
and chromatin modification-associated proteins. 44,45 is dispensable for proliferation using several established
Overexpression of Dtl promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cancer cell lines, yet its knockdown reduced tumorigenesis
(HCC) proliferation and invasion in vitro and in vivo, potentially through altered chromatin accessibility.
58
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 79 doi: 10.36922/gtm.6027