Page 38 - IJAMD-2-1
P. 38
International Journal of AI for
Materials and Design
ML molecular modeling of Ru: A KAN approach
A B
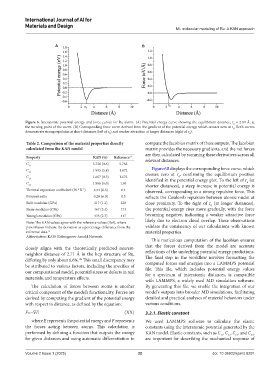
Figure 6. Interatomic potential energy and force curves for Ru atoms. (A) Potential energy curve showing the equilibrium distance, r ≈ 2.89 Å, at
0
the turning point of the curve. (B) Corresponding force curve derived from the gradient of the potential energy, which crosses zero at r . Both curves
0
demonstrate strong repulsion at short distances (left of r ) and weaker attraction at longer distances (right of r ).
0 0
Table 2. Comparison of the material properties directly compute the Jacobian matrix of these outputs. The Jacobian
calculated from the KAN model matrix provides the necessary gradients, and the net forces
are then calculated by summing these derivatives across all
Property KAN (%) Reference 51 relevant distances.
C 11 5.726 (0.6) 5.763
C 12 1.995 (5.8) 1.872 Figure 6B displays the corresponding force curve, which
C 1.667 (0.3) 1.673 crosses zero at r , confirming the equilibrium position
0
13 identified in the potential energy plot. To the left of r (at
C 1.966 (6.0) 1.84 0
44 shorter distances), a steep increase in potential energy is
Thermal expansion coefficient (10 K ) 6.44 (0.6) 6.4 observed, corresponding to a strong repulsive force. This
-6
-1
Poisson’s ratio 0.28 (6.0) 0.3 reflects the Coulomb repulsion between atomic nuclei at
Bulk modulus (GPa) 217 (1.3) 220 close proximity. To the right of r (at longer distances),
0
Shear modulus (GPa) 167 (3.4) 173 the potential energy rises more gradually, with the force
Young’s modulus (GPa) 435 (2.7) 447 becoming negative, indicating a weaker attractive force
Note: The KAN values agree with the reference values (Ref), where likely due to electron cloud overlap. These observations
parentheses indicate the deviation as a percentage difference from the validate the consistency of our calculations with known
reference data. 51 material properties.
Abbreviation: KAN: Kolmogorov-Arnold Network.
This meticulous computation of the Jacobian ensures
closely aligns with the theoretically predicted nearest- that the forces derived from the model are accurate
neighbor distance of 2.71 Å in the hcp structure of Ru, reflections of the underlying potential energy predictions.
differing by only about 6.6%. This small discrepancy may The final step in the workflow involves formatting the
38
be attributed to various factors, including the specifics of computed forces and energies into a LAMMPS potential
file. This file, which includes potential energy values
our computational model, potential stress or defects in real for a spectrum of interatomic distances, is compatible
materials, and temperature effects.
with LAMMPS, a widely used MD simulation software.
The calculation of forces between atoms is another By generating this file, we enable the integration of our
critical component of the model’s functionality. Forces are model’s outputs into broader MD simulations, facilitating
derived by computing the gradient of the potential energy detailed and practical analyses of material behaviors under
with respect to distance, as defined by the equation: various conditions.
F=−∇E (ⅩⅩ) 3.2.1. Elastic constant
where represents the potential energy and represents We used LAMMPS software to calculate the elastic
the forces acting between atoms. This calculation is constants using the interatomic potential generated by the
performed by defining a function that outputs the energy KAN model. Elastic constants, such as , , , and ,
13
44
12
11
for given distances and using automatic differentiation to are important for describing the mechanical response of
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 32 doi: 10.36922/ijamd.8291