Page 62 - IJAMD-2-3
P. 62
International Journal of AI for
Materials and Design Intelligent interactive textile in healthcare
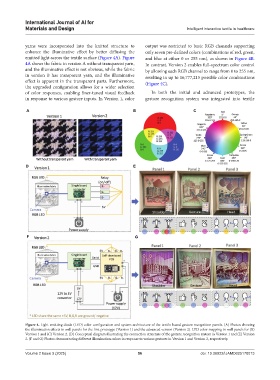
yarns were incorporated into the knitted structure to output was restricted to basic RGB channels supporting
enhance the illuminative effect by better diffusing the only seven pre-defined colors (combinations of red, green,
emitted light across the textile surface (Figure 4A). Figure and blue at either 0 or 255 nm), as shown in Figure 4B.
4A shows the fabric in version A without transparent yarn, In contrast, Version 2 enables full-spectrum color control
and the illuminative effect is not obvious, while the fabric by allowing each RGB channel to range from 0 to 255 nm,
in version B has transparent yarn, and the illuminative resulting in up to 16,777,215 possible color combinations
effect is apparent in the transparent parts. Furthermore, (Figure 4C).
the upgraded configuration allows for a wider selection
of color responses, enabling finer-tuned visual feedback In both the initial and advanced prototypes, the
in response to various gesture inputs. In Version 1, color gesture recognition system was integrated into textile
A B C
D E
F G
Figure 4. Light-emitting diode (LED) color configuration and system architecture of the textile-based gesture recognition panels. (A) Photos showing
the illumination effects in wall panels for the first prototype (Version 1) and the advanced version (Version 2). LED color mapping in wall panels for (B)
Version 1 and (C) Version 2. (D) Conceptual diagram illustrating the connection structure of the gesture recognition system in Version 1 and (E) Version
2. (F and G) Photos demonstrating different illumination colors in response to various gestures in Version 1 and Version 2, respectively.
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 56 doi: 10.36922/IJAMD025170013