Page 118 - IJB-10-1
P. 118
International Journal of Bioprinting Droplet-based bioprinting of tumor spheroids
Table 1. Summary of droplet-based bioprinting technologies
Droplet-based bioprinting Main process Droplet Cell viability Advantages Disadvantages
method parameters diameter (%)
(μm)
Thermal inkjet bioprinting Heat 30–60 75–90 Low cost and high Low cell viability and ease of
throughput clogging with viscous bioinks
Piezoelectric inkjet Waveform, 25–100 70–90 Wide range of droplet diam- Large shear stress due to rapid
bioprinting amplitude, and eter and low voltage change of pressure, satellite
frequency of droplets, and nozzle clogging
voltage pulse with viscous bioinks
Electrostatic bioprinting Frequency of 10–60 ~70 High throughput (up Low cell viability
voltage pulse, vis- to 2 kHz), suitable for
cosity of bioink high-viscous bioink, and
high precision
Electrohydrodynamic jet Voltage, flow rate, 10–1000 >90 (~95) Low shear stress, adapting Requirement of high voltage
bioprinting distance between to highly viscous bioinks, (5–20 kV), multiple droplets
nozzle tip and and a wide range of droplet ejection, and specialized
substrate diameter substrate
Microvalve-based Pneumatic 100–600 85–95 High cell viability, high fre- Large droplet diameter and high
bioprinting pressure, valve quency (up to 1 kHz), and a shear stress
gating time, wide range of viscosity
nozzle length,
and geometry
Acoustic Amplitude and 10–200 >90 (90–99) Nozzle-free, no clogging, no Complex structures and
bioprinting frequency of mechanical stress on cells, complicated operations
acoustic wave and large spray angle
Microfluidic bioprinting Flow rate, >10 >95 Droplet generation at high Polydimethylsiloxane (PMDS) is
hydrophilicity/ throughput, controlled prone to penetration, aging with
hydrophobicity of composition of droplets, poor thermal stability
pipeline and miniaturization
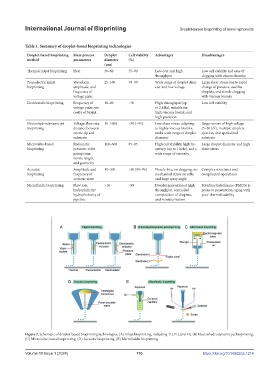
Figure 2. Schematic of droplet-based bioprinting technologies. (A) Inkjet bioprinting, including TIJ, PIJ, and EIJ. (B) Electrohydrodynamic jet bioprinting.
(C) Microvalve-based bioprinting. (D) Acoustic bioprinting. (E) Microfluidic bioprinting.
Volume 10 Issue 1 (2024) 110 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.1214