Page 139 - IJB-10-1
P. 139
International Journal of Bioprinting Bioprinting organoids for toxicity testing
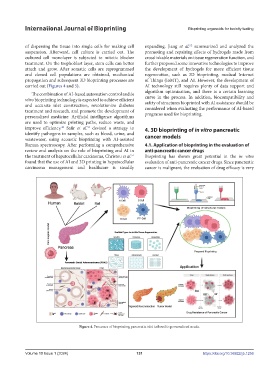
of dispersing the tissue into single cells for making cell expanding. Jiang et al. summarized and analyzed the
52
suspension. Afterward, cell culture is carried out. The promoting and repairing effects of hydrogels made from
cultured cell monolayer is subjected to mitotic blocker crosslinkable materials on tissue regeneration function, and
treatment. On the trophoblast layer, stem cells can better further proposed some innovative technologies to improve
attach and grow. After somatic cells are reprogrammed the development of hydrogels for more efficient tissue
and cloned cell populations are obtained, mechanical regeneration, such as 3D bioprinting, medical Internet
propagation and subsequent 3D bioprinting processes are of Things (IoMT), and AI. However, the development of
carried out (Figures 4 and 5). AI technology still requires plenty of data support and
The combination of AI-based automation control and in algorithm optimization, and there is a certain learning
vitro bioprinting technology is expected to achieve efficient curve in the process. In addition, biocompatibility and
and accurate islet construction, revolutionize diabetes safety of structures bioprinted with AI assistance should be
treatment and research, and promote the development of considered when evaluating the performance of AI-based
personalized medicine. Artificial intelligence algorithms programs used for bioprinting.
are used to optimize printing paths, reduce waste, and
improve efficiency. Safir et al. devised a strategy to 4. 3D bioprinting of in vitro pancreatic
50
49
identify pathogens in samples, such as blood, urine, and
wastewater, using acoustic bioprinting with AI-assisted cancer models
Raman spectroscopy. After performing a comprehensive 4.1. Application of bioprinting in the evaluation of
review and analysis on the role of bioprinting and AI in anti-pancreatic cancer drugs
the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma, Christou et al. Bioprinting has shown great potential in the in vitro
51
found that the use of AI and 3D printing in hepatocellular evaluation of anti-pancreatic cancer drugs. Since pancreatic
carcinoma management and healthcare is steadily cancer is malignant, the evaluation of drug efficacy is very
Figure 4. Processes of bioprinting pancreatic islet tailored to personalized needs.
Volume 10 Issue 1 (2024) 131 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.1256