Page 372 - IJB-10-1
P. 372
International Journal of Bioprinting Transdermal vitamin C delivery by MNPs
3.6. In vivo evaluation of MNPs efficacy in a photodamage, like collagen fiber disorder in the dermis,
photodamage mouse model elastic fiber breakdown, and sunburn cell development in the
Vitamin C was selected as a model drug for treating epidermis. Among them, sunburn cell formation was an
34
photodamage because of its antioxidant and poor important indicator of UVB irradiation damage. To avoid
35
absorption properties. The disease model of mice was epithelial cancer associated with excessive UVB exposure,
established with a UVB lamp. As shown in Figure 6a, the skin produces sunburn cells, which are apoptotic
treatment was administered to the mice by smearing the keratinocytes that offer protection in the epidermis.
drug with cotton swabs within the ring-restricted areas. In
the group receiving vitamin C by means of MNPs-assisted The results showed that other experimental groups had
delivery, the treated area had a clear treatment effect, and relatively severe skin photodamage symptoms, except for the
the surrounding untreated area had similar photodamage group receiving vitamin C by MNPs-assisted delivery, and
symptoms as the other groups (Figure 6b). we could observe tissue damage, inflammation, and sunburn
In addition to the macroscopic experimental results, we cells in these groups (Figure 6c). Our findings suggested
evaluated the microscopic histological condition of mice’s that MNPs-assisted transdermal vitamin C delivery showed
skin. Short-term high-dose UVB radiation causes acute skin significant therapeutic benefits in the mice model.
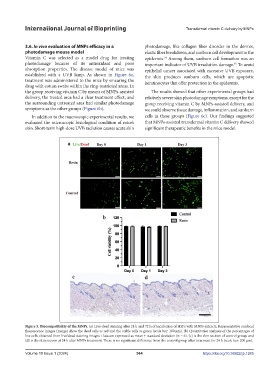
Figure 5. Biocompatibility of the MNPs. (a) Live-dead staining after 24 h and 72 h of incubation of HSFs with MNPs extracts. Representative confocal
fluorescence images (merge) show the dead cells as red and the viable cells as green (scale bar: 100 μm). (b) Quantitative analyses of the percentages of
live cells obtained from live/dead staining images. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). (c) is the skin section of control group, and
(d) is the skin section at 24 h after MNPs treatment. There is no significant difference from the control group after treatment for 24 h (scale bar: 200 μm).
Volume 10 Issue 1 (2024) 364 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.1285