Page 373 - IJB-10-1
P. 373
International Journal of Bioprinting Transdermal vitamin C delivery by MNPs
4. Discussion Recently, MNPs for promoting skin penetration have
attracted increasing attention due to their promising
People often suffer from excessive UVB irradiation in
their daily lives. Vitamin C is a well-known antioxidant application prospects and the fact that they can be applied
29
with photoprotection, and it is widely used in cosmetics to large and curved skin without any auxiliary devices.
due to its reliable skincare benefits. However, delivery MNPs hold great application potential for enhancing the
of vitamin C through traditional approaches (creams, transdermal drug delivery. Topical formulation containing
emulsions and lotions) limits its effectiveness because MNPs is a widely applied method because it is convenient
of its low permeability in the skin. Therefore, it is and patient-compliant. The recently reported fabrication
36
imperative to develop efficient transdermal vitamin C methods of MNPs are mainly conventional subtractive
delivery routes. manufacturing and formative manufacturing. However,
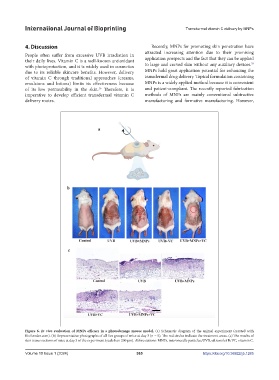
Figure 6. In vivo evaluation of MNPs efficacy in a photodamage mouse model. (a) Schematic diagram of the animal experiment (created with
BioRender.com). (b) Representative photographs of all five groups of mice at day 3 (n = 5). The red circles indicate the treatment areas. (c) The results of
skin tissue sections of mice at day 3 of the experiment (scale bar: 200 μm). Abbreviations: MNPs, microneedle particles; UVB, ultraviolet B; VC, vitamin C.
Volume 10 Issue 1 (2024) 365 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.1285