Page 142 - IJB-10-2
P. 142
International Journal of Bioprinting dECM bioink for in vitro disease modeling
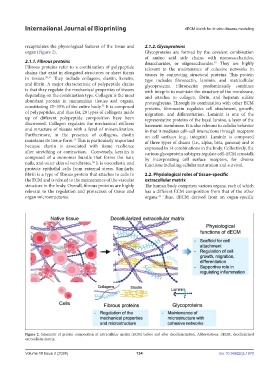
recapitulates the physiological features of the tissue and 2.1.2. Glycoproteins
organ (Figure 2). Glycoproteins are formed by the covalent combination
of amino acid side chains with monosaccharides,
2.1.1. Fibrous proteins disaccharides, or oligosaccharides. They are highly
35
Fibrous proteins refer to a combination of polypeptide relevant to the maintenance of cohesive networks in
chains that exist in elongated structures or sheet forms tissues by connecting structural proteins. This protein
in tissues. 30,31 They include collagens, elastin, keratin, type includes fibronectin, laminin, and matricellular
and fibrin. A major characteristic of polypeptide chains glycoproteins. Fibronectin predominantly combines
is that they regulate the mechanical properties of tissues with integrin to maintain the structure of the membrane,
depending on the combination type. Collagen is the most and attaches to collagen, fibrin, and heparan sulfate
abundant protein in mammalian tissues and organs, proteoglycans. Through its combination with other ECM
constituting 25–35% of the entire body. It is composed proteins, fibronectin regulates cell attachment, growth,
32
of polypeptides, and thus far, 28 types of collagens made migration, and differentiation. Laminin is one of the
up of different polypeptide composition have been representative proteins of the basal lamina, a layer of the
discovered. Collagen regulates the mechanical stiffness basement membrane. It is also relevant to cellular behavior
and structure of tissues with a level of mineralization. in that it mediates cell–cell interactions through receptors
Furthermore, in the presence of collagens, elastin on cell surfaces (e.g., integrin). Laminin is composed
maintains its tissue form. This is particularly important of three types of chains (i.e., alpha, beta, gamma) and is
33
because elastin is associated with tissue resilience expressed in 14 combinations in the body. Collectively, the
after stretching or contraction. Conversely, keratin is various glycoprotein subtypes regulate cell–ECM crosstalk
composed of a monomer bundle that forms the hair, by incorporating cell surface receptors, for diverse
nails, and outer skin of vertebrates. It is viscoelastic and functions including cellular maturation and survival.
34
protects epithelial cells from external stress. Similarly,
fibrin is a type of fibrous protein that attaches to cells in 2.2. Physiological roles of tissue-specific
the ECM and is related to the maintenance of the vascular extracellular matrix
structure in the body. Overall, fibrous proteins are highly The human body comprises various organs, each of which
relevant to the regulation and protection of tissue and has a different ECM composition from that of the other
organ microstructures. organs. Thus, dECM derived from an organ-specific
36
Figure 2. Schematic of protein composition of extracellular matrix (ECM) before and after decellularization. Abbreviations: dECM, decellularized
extracellular matrix.
Volume 10 Issue 2 (2024) 134 doi: 10.36922/ijb.1970