Page 202 - IJB-10-2
P. 202
International Journal of Bioprinting Optimizing inkjet bioprinting
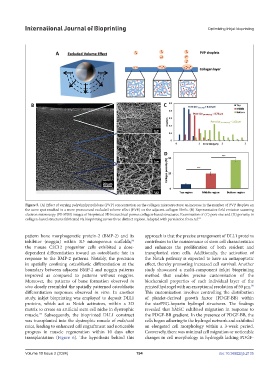
Figure 5. (A) Effect of varying polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) concentration on the collagen microstructure; an increase in the number of PVP droplets on
the same spot resulted in a more pronounced excluded volume effect (EVE) on the adjacent collagen fibrils. (B) Representative field emission scanning
electron microscopy (FE-SEM) images of bioprinted 3D hierarchical porous collagen-based structures. Examination of (C) pore size and (D) porosity in
collagen-based structures fabricated via bioprinting across three distinct regions. Adapted with permission from ref.
91
pattern bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) and its approach is that the precise arrangement of DLL1 proteins
96
inhibitor (noggin) within 3D microporous scaffolds; contributes to the maintenance of stem cell characteristics
the mouse C2C12 progenitor cells exhibited a dose- and enhances the proliferation of both resident and
dependent differentiation toward an osteoblastic fate in transplanted stem cells. Additionally, the activation of
response to the BMP-2 patterns. Notably, the precision the Notch pathway is expected to have an antiapoptotic
in spatially confining osteoblastic differentiation at the effect, thereby promoting increased cell survival. Another
boundary between adjacent BMP-2 and noggin patterns study showcased a multi-component inkjet bioprinting
improved as compared to patterns without noggins. method that enables precise customization of the
Moreover, the patterns of bone formation observed in biochemical properties of each individual layer of the
98
vivo closely resembled the spatially patterned osteoblastic printed hydrogel with an exceptional resolution of 50 µm.
differentiation responses observed in vitro. In another This customization involves controlling the distribution
study, inkjet bioprinting was employed to deposit DLL1 of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF-BB) within
proteins, which act as Notch activators, within a 3D the starPEG-heparin hydrogel structures. The findings
matrix to create an artificial stem cell niche in dystrophic revealed that hMSC exhibited migration in response to
muscle. Subsequently, the bioprinted DLL1 construct the PDGF-BB gradient. In the presence of PDGF-BB, the
97
was transplanted into the dystrophic muscle of mdx/scid cells began adhering to the hydrogel network and exhibited
mice, leading to enhanced cell engraftment and noticeable an elongated cell morphology within a 3-week period.
progress in muscle regeneration within 10 days after Conversely, there was minimal cell migration or noticeable
transplantation (Figure 6). The hypothesis behind this changes in cell morphology in hydrogels lacking PDGF-
Volume 10 Issue 2 (2024) 194 doi: 10.36922/ijb.2135